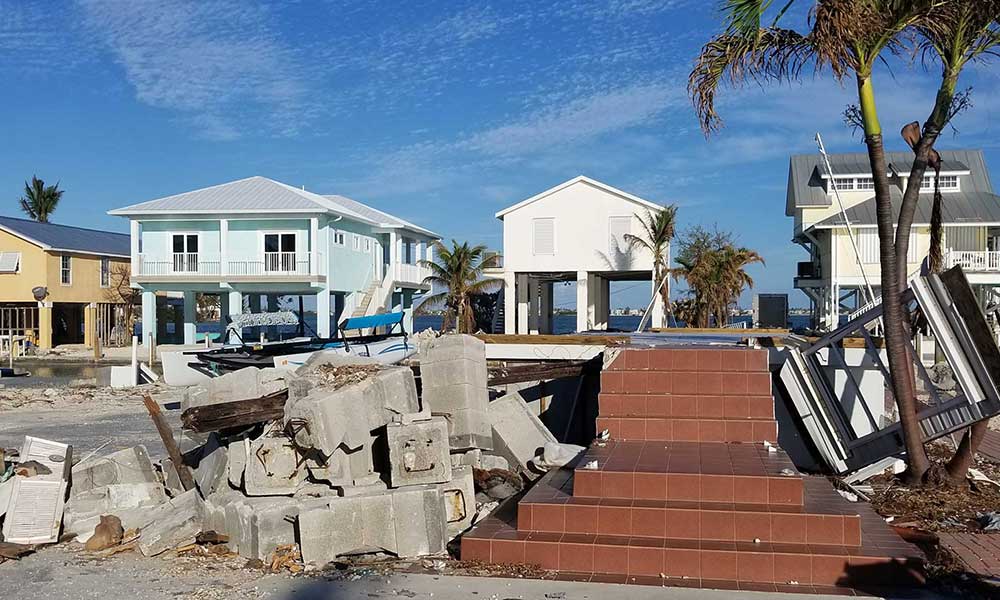
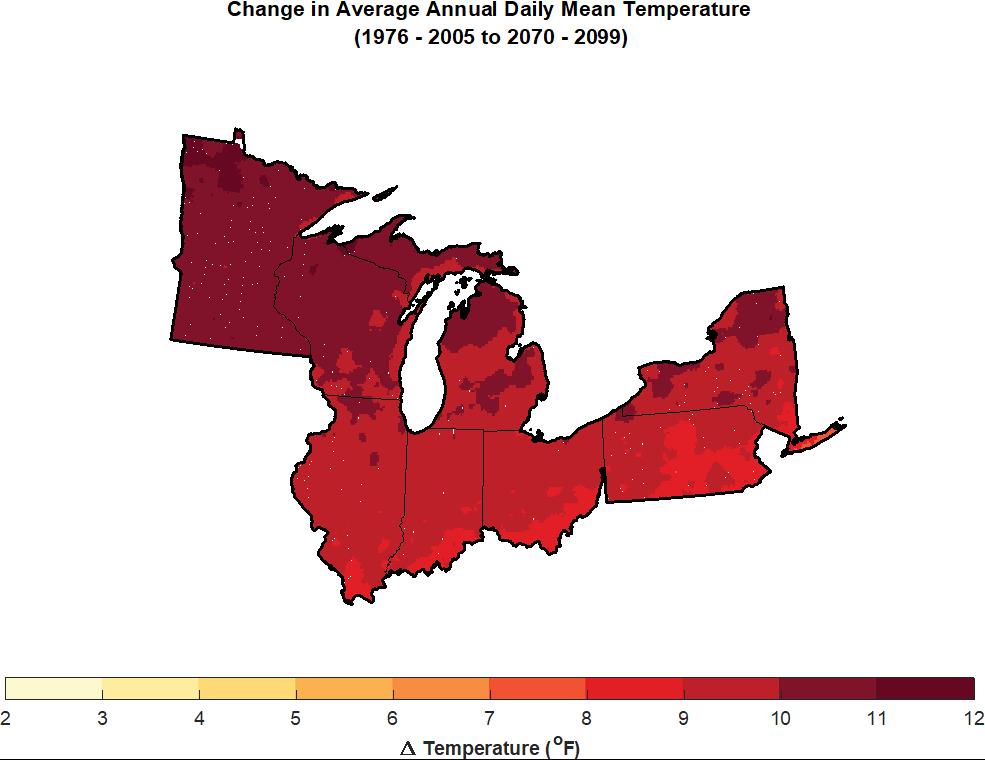
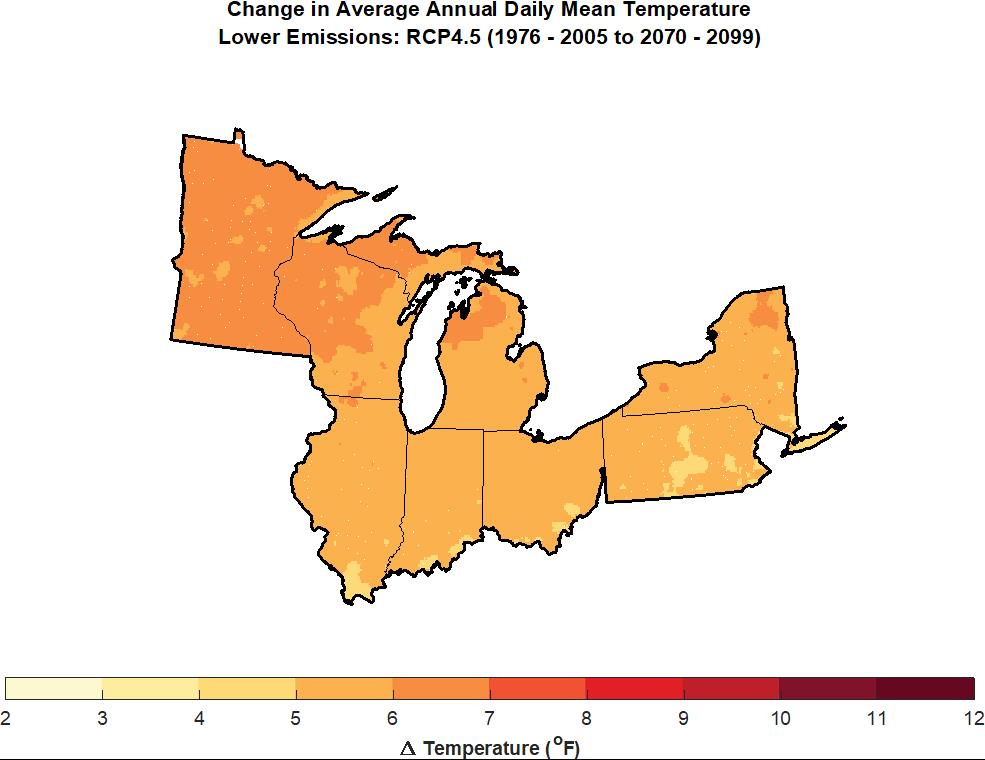
President Joe Biden’s $2.3 trillion infrastructure bill aims to fix much that is ailing in America, and its sheer size is drawing predictable—and short-sighted—fire from Republicans in Congress. The nation has a great deal of aging infrastructure, which will eventually pose a massive challenge to economic development. But the American Jobs Plan also takes aim at a growing, urgent, and critical need for infrastructure to cope with the impacts of climate change. These affect many kinds of infrastructure, including transportation, water, wastewater, and energy and communications systems. There is nothing patriotic, it seems to me, in being so oppositional as to allow our nation to deteriorate, Texas-style, in the face of changing climate conditions. There is also nothing about what happened in Texas with frozen energy systems that contradicts “global warming.” The research clearly shows that climate instability, including seemingly less predictable winter storms, is part of the overall impact of a generally warming climate. Nobody but a charlatan ever promised that climate change would be a simple topic.
President Joe Biden’s $2.3 trillion infrastructure bill aims to fix much that is ailing in America, and its sheer size is drawing predictable—and short-sighted—fire from Republicans in Congress. The nation has a great deal of aging infrastructure, which will eventually pose a massive challenge to economic development. But the American Jobs Plan also takes aim at a growing, urgent, and critical need for infrastructure to cope with the impacts of climate change. These affect many kinds of infrastructure, including transportation, water, wastewater, and energy and communications systems. There is nothing patriotic, it seems to me, in being so oppositional as to allow our nation to deteriorate, Texas-style, in the face of changing climate conditions. There is also nothing about what happened in Texas with frozen energy systems that contradicts “global warming.” The research clearly shows that climate instability, including seemingly less predictable winter storms, is part of the overall impact of a generally warming climate. Nobody but a charlatan ever promised that climate change would be a simple topic.
Earlier this year, I reviewed a book by a former Toronto mayor about what cities are doing about climate change. Later, I reviewed Doug Farr’s elaborate tome on how the design professions are providing solutions to climate challenges in new forms of housing and urban development. In addition, a year ago, I reviewed a new Planning Advisory Service Report by the American Planning Association on planning for infrastructure resilience. I remain committed to highlighting resources for planners, public officials, and interested citizens on issues of climate resilience.
In this post, I feature a new book on community solutions to climate resilience. In Harm’s Way, by John Cleveland and Peter Plastrik, provides a set of detailed ideas for building climate resilience in our communities. In my view, its dominant values in contributing to the discussion of climate change and community adaptation center on two crucial issues: first, how to finance investments in climate resilience, and second, how to build the policy foundations for managing retreat from the most vulnerable coastal areas as a means of avoiding major “natural” disasters. The two co-authors bring interesting backgrounds for such discussion. Cleveland is executive director of the Innovation Network for Communities (INC) and a member of the Boston Green Ribbon Commission, a group of business and civic leaders supporting the Boston Climate Action Plan. Plastrik is vice-president of INC and co-author of an Island Press book on networking for social change.
The Biden plan faces a challenging uphill climb toward passage in Congress. The money it promises for what it offers to do is heavily dependent on changes in corporate taxation that may face daunting opposition in Congress. In any case, even passage of the plan does not necessarily mean that every valuable potential investment at the local level in more resilient infrastructure will be assured of adequate funding, nor does it mean that local leaders will always agree with federal priorities for their own communities. The struggle to implement the plan will face years of challenges. In short, this is an important time for the vital discussion by Cleveland and Plastrik on how we can best find the money for essential investments in climate resilience.
Financing climate resilience is essentially an exercise in risk management. The first ingredient in successful risk management is recognition of the problem, which at a national scale has been a political football because of right-wing denial that a problem exists. For four years, this denial was centered in the White House, but the nation clearly chose a sea change on climate policy in the 2020 election. But that does not mean that nothing was happening outside the Trump administration—far from it. Local financial innovations were afoot in numerous American communities, including large cities like Boston, Miami, and San Francisco. Indeed, networks of such cities have been exploring avenues for fostering climate-related investments. The issue in many cases, because local governments seldom have large stores of cash awaiting brilliant ideas, is hunting for money in the financial markets. In many ways, the hunt for climate-resilient investments is a race against time for cities that may face climate-related disasters that may cost far more in damages than the investments they are contemplating to prevent such outcomes. Misalignments between resources and needs are commonplace, the environmental burdens of climate change, particularly on low-income and minority neighborhoods, are often enormous, and public revenue is often insufficient to address the problem. The authors thus focus on the need for innovations in climate resilience finance to meet this challenge. Given the likelihood that at least some of the Biden plan will require some level of local and state matching funds, this issue will remain potent. The authors outline a range of tools for creating these new financial structures. This task is far from impossible, however. Bond-rating firms and others are already recognizing the inherent risks involved in ignoring climate change. Why not invest on the positive side through mitigation and adaptation?
Case studies are always helpful in making clear that some community, somewhere, is at least testing solutions, many of them proving successful. The authors outline a playbook for paying for climate resilience, using eight examples in which communities have generated local revenue, imposed land-use costs on unwise development, leveraged development opportunities to achieve climate resilience, and pursued equity, among other options. Local governments in fact have a range of regulatory tools and incentives they use to leverage many other decisions by businesses and residents, many of the options, such as floodplain management rules, are already common. What is needed is the imagination for new ideas on how to use those tools, as well as accessible guidance on how well those ideas are working and under what circumstances. One city highlighted in this chapter is Norfolk, Virginia, a low-lying city on the Atlantic coast that faces a future laden with nuisance flooding due to sea level rise. Its system of four color-coded zones indicates relative levels of safety or vulnerability as a means of directing redevelopment to safer areas while demarcating those in need of protection. Zoning may not seem like a financial issue, but it is a quintessential financial tool in dictating what sort of development is permissible in what location, thus channeling investment to those areas the city deems acceptable for certain purposes. The problem is that the power of zoning has not always been used with a vivid awareness of the environmental hazards that are tied to urban geography.
In the U.S. system, municipalities are creations of the states, which establish the rules under which cities operate. Notwithstanding the magnitude of federal largesse, it is thus also fitting that the book contains a chapter on how states can help communities invest in climate resilience. States can serve as both barriers to and intentional supporters of local innovations in financing climate resilience.

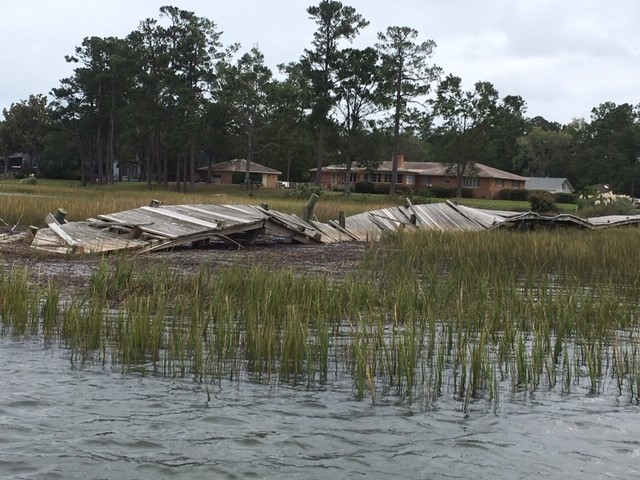
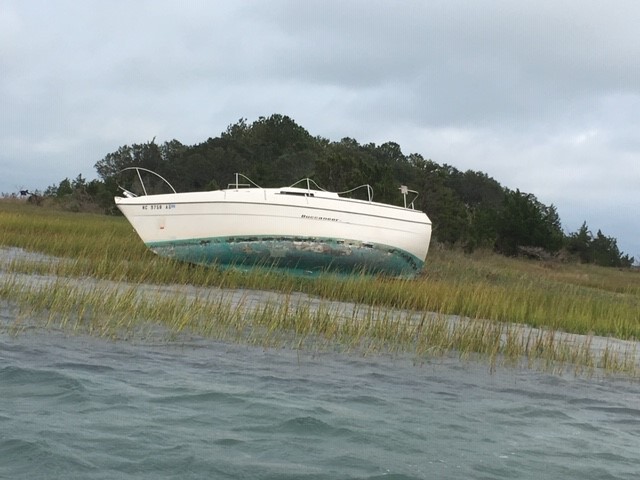
Collapsed houses after Hurricane Sandy on the Jersey shore. The results of climate-driven disasters are seldom pretty.
In the end, however, all of this depends to some degree on political will, a subject addressed in a final chapter on managed retreat under the caption, “Can it happen here?” Communities have long shied away from open discussion of retreat from the shoreline or highly volatile riverfronts. Seashore land has historically been some of the most valuable real estate in the nation, and not only because it can become a haven for rich owners of second homes, but because beaches attract tourism and harbors attract economic development and transportation infrastructure. What public official wants to say no to new shoreline development, let alone talk of managing retreat from existing settlements? Yet the sheer long-term cost of such reluctance to lead with courage is something I discussed in another book review early last year. The Geography of Risk was a book that detailed wave after wave of catastrophic destruction on the New Jersey barrier islands as a result of investments by entrenched real estate interests that resisted risk-based land-use reforms.
But Cleveland and Plastrik insist that retreat will happen, and the question is not if, but when, and under what circumstances. Basically, they say, in coastal areas threatened by climate change and sea level rise, retreat will be driven either by disasters, or by the market, or by plans. In the first instance, nature itself will make decisions that force painful choices that we cannot control. In the second, recognizing the inherent dangers of such stubborn persistence, market forces will withdraw investment from areas that are no longer viable as a result of climate change, with major losses for those who either lack the means to move or who fail to read the tea leaves. The final choice, plan-driven retreat, is the only one that allows the community some degree of sovereignty in the matter, deliberating about the direction of retreat, the means of financing it, and ways of mitigating financial consequences for those involved. The problem is finding articulate, visionary leadership that can lead the community to its moment of truth.
Jim Schwab