
Photo by Jeff Clevenger
We learn from disasters as we recover from them, but each disaster teaches slightly different things. Sometimes the lessons are significant and historic; in others, one community is learning what others already know or should have learned from their own past events. Some years are relatively quiescent, as 2018 so far seems to be. And some become relentless slogs, like 2017.
Adam Smith, lead scientist for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s National Centers for Environmental Information, noted in a plenary panel in July for the 2018 Natural Hazards Workshop, in Broomfield, Colorado, that the tally for 2017 disasters had exceeded $200 billion. This is more than 40 percent of the tally so far of billion-dollar disasters for the entire decade beginning in 2010. Simply put, with three major hurricanes—Harvey, Irma, and Maria—striking parts of the southern U.S., followed in short order by some of the most expensive wildfires in California history, it was a wild, taxing year in the world of emergency management.
But our attention fades quickly. Right now, there are no equivalent disasters seizing our attention, but in time there will be. The people who remain painfully aware that recovery is a long, slow process are those directly affected, and even many of them will not fully grasp the ways in which past location choices and patterns of development have brought them to this pass. Many had no choice anyway. Our communities are frequently full of social inequities that compromise the life choices of the poor and disabled. In other cases, the losses inflicted on neighborhoods are the result of hubris on the part of developers, city officials, and homeowners themselves. It does not hurt, approximately one year after these combined events, to look at what we know so far about the recovery following them.
Apparently, the U.S. General Accountability Office (GAO), an arm of Congress, agreed that the time was ripe for review because it has released a study, 2017 Hurricanes and Wildfires: Initial Observations on the Federal Response and Key Recovery Challenges. Because of the severity of challenges in Puerto Rico, one may note from the graph below, reproduced from the report, that Hurricane Maria by far entailed the largest federal expenditures.
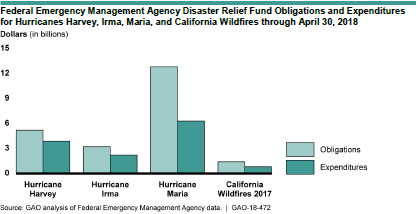 In spite of that level of effort, Puerto Rico has engendered the most significant criticism of the performance of the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). Maria struck Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands (USVI) after Harvey had already drenched and flooded coastal Texas, and Irma had swept through much of Florida.
In spite of that level of effort, Puerto Rico has engendered the most significant criticism of the performance of the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). Maria struck Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands (USVI) after Harvey had already drenched and flooded coastal Texas, and Irma had swept through much of Florida.

FEMA teams managing the distribution of water, and meals for hundreds of semi-trucks at an incident Support Base in Seguin, Texas. Photo by Dominick Del Vecchio – Aug 29, 2017
The report notes that, as a result, FEMA resources were severely stretched by then, only to have wildfires in California add to the pressure, though the personnel assigned in the last case were small compared to the hurricanes (as is typically the case). Adding to the challenge, Puerto Rico and USVI are offshore and were also poorly prepared for a Category 4 hurricane. Puerto Rico had already suffered years of neglect of crucial infrastructure, was burdened with oppressive debts, and was by far the least prosperous target of the 2017 storms. All this, combined with some incredibly inept public relations from the White House, led to a perfect storm in which nearly 3,000 people have died directly or indirectly as a result of the disaster. To my knowledge, that is a number exceeded in U.S. history only by the 1900 hurricane in Galveston, which killed more than twice as many people. The difference is that, in Puerto Rico, most people died because of blocked transportation, loss of electricity, and similar problems with critical facilities that prevented adequate transportation or medical attention in many isolated communities in the interior of the mountainous island.
Exactly what we learn from Puerto Rico remains to be seen. It is worth noting, in my view, that far more prosperous Hawaii has coped well with admittedly less-challenging disasters in recent years, in large part because state government has practiced response and committed resources to the problem. I say this despite being aware of gaps in Hawaii recovery planning that merit further attention. But if Puerto Rico is a logistical challenge for mainland responders, Hawaii is even more remote but better prepared. The difference in economic circumstances, however, is a dramatic and powerful variable in this comparison, as is Hawaii’s statehood. It is also worth noting that Hawaii is a long chain of islands, and storms (or volcanoes) never affect all at the same time. Effectively, that has always meant that emergency resources in Hawaii have been able to be moved from one or more islands to another that has been hit by a storm. All of Puerto Rico was devastated almost on the same day, with internal transportation, communications, and electric power nearly brought to a standstill, making access to many villages nearly impossible.
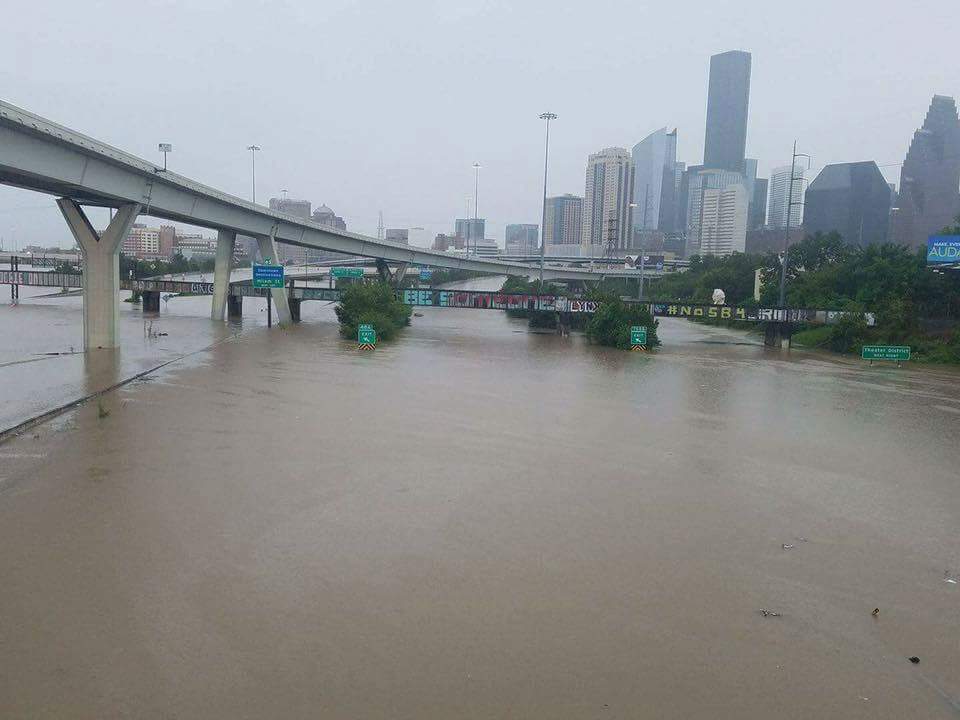
If Puerto Rico, followed closely by USVI, is the direst case for long-term recovery, there nonetheless remain serious challenges in Texas, not only in Houston but in dozens of other counties along the Gulf Coast. A recent Washington Post article used the term “Harvey homeless” to describe thousands of Texas families living in whatever parts of their flooded homes they have salvaged while struggling to accumulate the resources to repair the rest. They live with mold, dust, and any other environmental contaminants that endure in essentially unusable parts of their homes. In all, according to the Texas Department of Public Safety, at least 175,000 Texas homes were “badly damaged” by Hurricane Harvey, and 80 percent lacked flood insurance, thus relying on much smaller federal disaster payments (averaging $4,203) than flood insurance would have afforded. If there is one powerful lesson in Texas, it concerns public education on the value of flood insurance, particularly in the many areas outside the 100-year floodplain.  Unfortunately, much of the public retains the illusion that flood insurance is either unnecessary or unavailable outside the legally defined floodplain. Yet Harvey’s 60 inches of rain in some parts of metropolitan Houston left vast areas beyond the regulatory flood boundaries under water because water does not care about such artificial boundaries. It goes where gravity compels it to go. Moreover, years of loose land-use regulation over the past half-century of rapid growth have expanded the floodplain and put numerous neighborhoods in greater danger than they faced in the past.
Unfortunately, much of the public retains the illusion that flood insurance is either unnecessary or unavailable outside the legally defined floodplain. Yet Harvey’s 60 inches of rain in some parts of metropolitan Houston left vast areas beyond the regulatory flood boundaries under water because water does not care about such artificial boundaries. It goes where gravity compels it to go. Moreover, years of loose land-use regulation over the past half-century of rapid growth have expanded the floodplain and put numerous neighborhoods in greater danger than they faced in the past.
Moreover, as John Henneberger, executive director of the nonprofit advocacy group Texas Housers, noted in his keynote at the Natural Hazards Workshop, Texas does not have a noteworthy history of attention to social equity in disaster recovery. Henneberger called for a new model of disaster recovery in which we seek to use recovery planning to overcome racial and economic inequities, stating that “the legal framework already exists” in federal programs like Community Development Block Grant—Disaster Recovery (CDBG-DR) to “overcome inequalities,” but the rules are not always followed. Thus, his top recommendation for reform was simply to “obey the law” regarding the conditions that apply to state and local use of CDBG-DR funds.
Finally, Bloomberg Business Week chose recently to examine the questions surrounding rebuilding after the California wildfires. With a population already approaching 40 million, the state is under intense pressure to build adequate housing amid rising housing costs. California has repeatedly toughened its building codes in response to wildfire threats but faces a legacy problem of homes built under earlier standards. Not often known outside wildfire research circles is the fact that the average home contains seven to eight times the density of combustible materials as the surrounding forest in the wildland-urban interface. That means that every home that catches fire or explodes is a huge matchstick endangering every other home in its immediate vicinity. When one considers that California is unquestionably the most progressive state in tackling wildfire problems, one understands that the problem of retrofitting older homes built to lower building code standards—or none at all in some other western states—is a lingering and potentially very expensive problem. The dilemma serves to illuminate the value of pre-planning for recovery, learning how to seize the “teachable moment” for reform, to reduce the scope of the problem. The article also notes that, if California is to reduce pressure to build in the forest, its cities must be prepared to allow greater density to relieve the housing crisis in a state where a shortage of affordable housing has yielded a concomitant problem of growing homelessness. And so, we see why urban planning needs both to be holistic in its approach to social problems and guided by wise state policy with supporting resources. We all still have a long way to go.
This blog post can never be long enough to explore all these issues in depth. But in coming weeks and months, I hope to delve into specific issues more deeply, share interviews with individual experts, and explore what needs to be done. I am also watching intently for new books that will shed light on new solutions. One just arrived today. Stay tuned.
Jim Schwab











