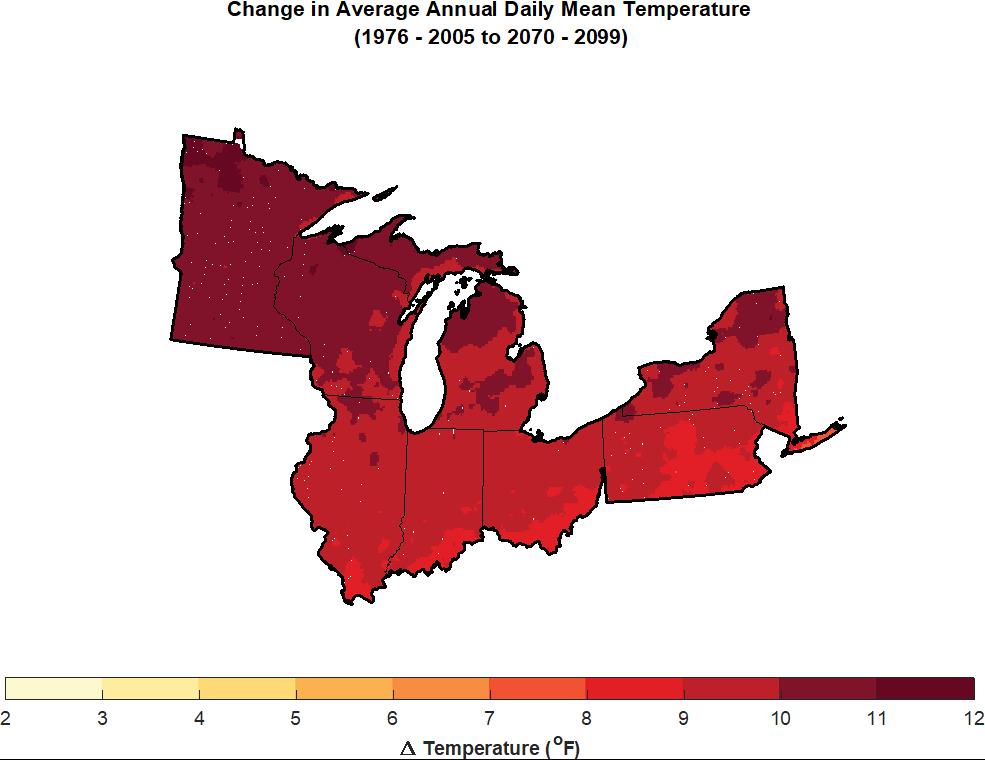
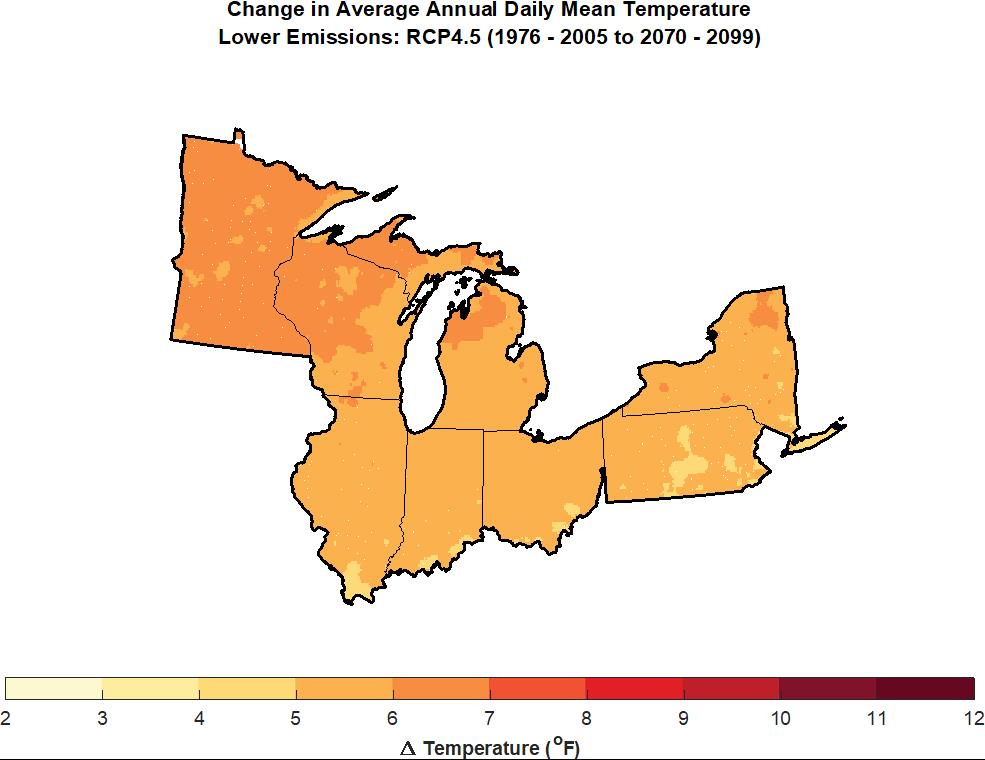
This summer, the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) is at last rolling out its Building Resilient Infrastructure and Communities (BRIC) program, and its first Notice of Funding Opportunity will likely be issued in September. In July, FEMA is airing a series of five weekly webinars to introduce BRIC to communities and state officials around the nation. BRIC is the practical result of provisions in the Disaster Recovery Reform Act, passed by Congress in 2018, to create a secure funding stream for what was formerly the Pre-Disaster Mitigation program. I plan to discuss all that in coming weeks on this blog.
This summer, the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) is at last rolling out its Building Resilient Infrastructure and Communities (BRIC) program, and its first Notice of Funding Opportunity will likely be issued in September. In July, FEMA is airing a series of five weekly webinars to introduce BRIC to communities and state officials around the nation. BRIC is the practical result of provisions in the Disaster Recovery Reform Act, passed by Congress in 2018, to create a secure funding stream for what was formerly the Pre-Disaster Mitigation program. I plan to discuss all that in coming weeks on this blog.
But the personal impact on me was to remind me to attend to an egregious oversight on my part that began earlier this year with the release by the American Planning Association (APA) of a new Planning Advisory Service Report, Planning for Resilient Infrastructure. I read it, attended to some other business in Texas and Nebraska in late February and early March, and along came the coronavirus, upending most of my existing personal and professional plans and refocusing my attention. But it is time for me to give this report the attention it deserves.
First, there is the question of why it deserves attention. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), which funded the project led by the Association of State Floodplain Managers (ASFPM), which partnered with APA, chose their joint proposal in funding the first round of projects under its Coastal Resilience Grants Program in 2016. As Jeffrey Payne, director of NOAA’s Office for Coastal Management, states in his preface, “Tomorrow isn’t what it used to be. Increasingly, coastal conditions include all the risks of the past, but risks that are amplified by a changing climate, rising seas, and more rapidly fluctuating Great Lakes.”
In the interest of full disclosure, I was involved with ASFPM executive director Chad Berginnis in co-authoring the proposal for this project in the summer of 2015. (After I left APA, ASFPM hired me back as a consultant in later stages of the effort to help refine and focus the PAS Report.) Our intent was both simple and bold. Local governments spend tens of billions of dollars annually on the construction and maintenance of various kinds of infrastructure. Much of that infrastructure, related to essential services including water, wastewater, and transportation, is subject to the impacts of climate change. While, as Payne goes on to state, this is true away from the coast as well, some of those impacts are particularly significant and noticeable in coastal states and communities. In short, a great deal of taxpayer money is at stake regarding the ability of that infrastructure to withstand future climate conditions and natural disasters. Planning for greatly increased resilience is a recipe for improved fiscal stability. This holds true even if, as planned by statute, a greater share of that funding for hazard mitigation projects comes from FEMA through BRIC. Taxpayers are taxpayers, whether the money used is federal, state, or local.
All that said, the serious work of completing the work fell to Joseph DeAngelis at APA, now the manager of the APA Hazards Planning Center, and Haley Briel, a research specialist for the Flood Science Center at ASFPM, along with Michael Lauer, a planning consultant with deep experience in growth management programs in southeastern coastal states.
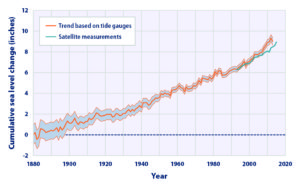
Global average sea level rise from 1880 to the present, based on tide gauges and satellite measurements (US EPA). Reuse courtesy of APA.
Their collaborative report addresses the most significant issues of infrastructure resilience. Particularly in areas subject to coastal storms, these involve not just the impacts of major disasters but the everyday nuisance impacts of flooding because of high tides atop sea level rise that already are yielding closed streets and parks and flooded basements. Urban flooding has become a “thing” where the term never used to be heard. They include a small table with projections by the U.S. Global Change Research Program showing ranges of sea level rise between 0.5 and 1.2 feet by 2050, and 1 to 4 feet by 2100. Of course, these are rough ranges in part because various geological conditions, such as erosion or glacial rebound, cause different results from one region to another, although most of the East Coast faces serious problems over the coming century. A major part of the problem is that sea level rise amplifies the impact of high tides in storms, leading to increased flooding and erosion that is already evident in low-lying cities like Norfolk, Virginia, or Miami. The authors note that, “Over the last half-century alone, with just one to three inches of average sea level rise, daily high-tide flooding has become up to 10 times more frequent” in American coastal communities. Even in Midwestern communities, including those along the Great Lakes, problems result from climate-driven increases in high-precipitation storms that frequently overwhelm stormwater drainage systems built in an earlier era based on other, less challenging, assumptions.
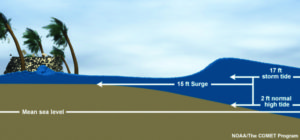
Storm surge heights are cumulatively based on the mean sea level, the height of the tide, and the high volume of water pushed toward the shore by coastal storms (National Hurricane Center). Reuse courtesy of APA.
It is natural that a planning document is going to assert a role for planners in addressing these problems. The role the report asserts is entirely logical, starting with “assessing long-term infrastructure needs and understanding future risks to infrastructure assets.” Equally logical, however, is that the report builds upon prior APA literature to outline the need for coordinated action through the plan-making process to integrate climate risk into local plans as a means of “capturing the future conditions to which existing infrastructure and any planned infrastructure projects will be subjected.” Put simply, if the local planning process does not identify those risks and provide clear recommendations for creating resilient infrastructure, it is not likely to materialize in any coherent and consistent fashion. The third chapter outlines a step-by-step approach (see illustrations below) for developing an inventory of local infrastructure, identifying risks, and moving toward an effective plan for adaptation.
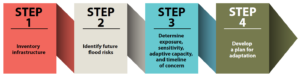
The process for conducting an infrastructure vulnerability assessment (Joseph DeAngelis). Reuse courtesy of APA for both diagrams.
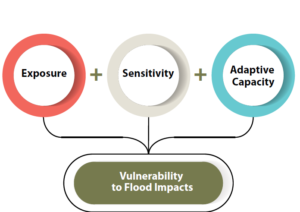
A project or asset’s vulnerability to flood impacts is a product of its exposure, sensitivity, and adaptive capacity (Joseph DeAngelis).
Later, the report provides some examples of what such consistent planning for resilient infrastructure may look like. Its case study of San Francisco’s approach to assessing sea-level-rise impacts outlines how the Sea Level Rise Committee of the city’s Capital Planning Committee (CPC), a body responsible for overseeing capital investments for infrastructure, recommended using the upper end of estimates from a National Research Council report for the West Coast. These were fed into a CPC guidance document for assessing vulnerability and supporting adaptation to sea level rise, a primary outcome of climate change. Without engaging the full details here, the bottom line is that the City and County of San Francisco was working from a single play book for climate adaptation of project life cycles for future infrastructure. Capital planning could thus proceed in a more standardized manner based on common assumptions. The report also uses an extensive example from Toledo, Ohio, the site of one of two pilot projects supported by the ASFPM/APA project. Toledo, sitting on the shores of Lake Erie, has suffered from stormwater flooding and is approaching the problem with a mixture of green infrastructure and analysis of social vulnerability in affected neighborhoods. The report elsewhere delves into questions and methods of documenting and addressing environmental justice and social and racial inequities in environmental protection through appropriate local capital planning projects.
Both cases highlight the value for local planners of establishing credible data sources, which often rest within federal agencies such as NOAA and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. But, as one chapter illustrates, these can include experienced national nonprofits as well, such as Climate Central. Unquestionably, however, the best single assemblage of data and tools is NOAA’s own Digital Coast website. Planners can access additional high-quality resources on climate through other NOAA programs such as the Regional Climate Centers, located at a series of universities across the nation, and the Regional Integrated Sciences and Assessments, where RISA staff work directly with climate scientists to communicate the science to the public and local officials.
Just as important as understanding where to find the proper data and tools, however, is a knowledge of best practices in local capital improvements planning, the development of effective standards, guidelines, and regulations for creating resilient infrastructure, and, finally, the best means for financing such long-term investments in infrastructure, especially with an eye to climate resilience. Each of these three topics is covered in separate chapters in the second half of the report.

View of part of the Jersey Shore after Hurricane Sandy, February 2013.
Ultimately, the real challenge for local planners is overcoming a natural discomfort with the inherent uncertainties in planning for infrastructure that must withstand the impacts of climate change within a range of assumptions that, in part, depend on federal and even international action to mitigate rising global temperatures as a result of greenhouse gas emissions. Planners, and the communities they serve, must adjust to those uncertainties and the inherent complexities they embody. Planning, however, has always been a speculative enterprise riddled by uncertainties, yet cities have embraced assumptions about population growth, demographic change, and economic scenarios that have often been equally uncertain, for none of us has a crystal ball. What we do know, however, is the direction of existing and accelerating trends, and climate change is no myth. We are ultimately better off, and will better invest public resources, by anticipating climate change with the best projections available, so that our communities are not overwhelmed by future storms, sea level rise, and storm surge. We cannot say we did not see it coming. We can only hope to say we used a wise approach based on the best data available to avoid catastrophe for ourselves and future generations in the communities we serve.
Jim Schwab