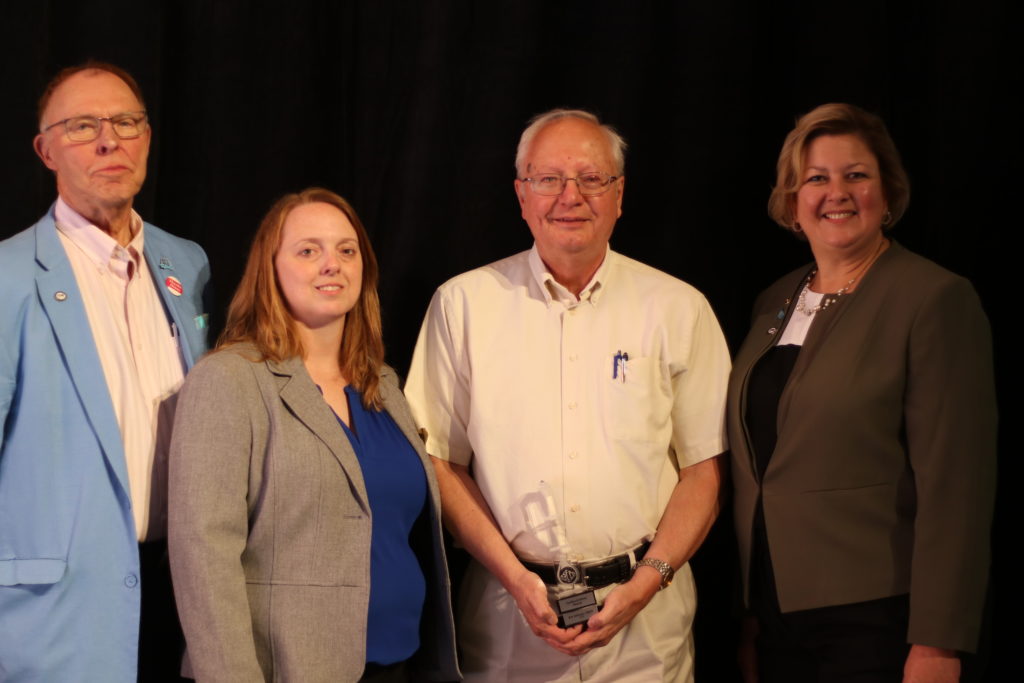
From left: Larry Larson; Maria Cox-Lamm, ASFPM Chair; myself; Ingrid Wadsworth, ASFPM Deputy Director
I confess: I was taken totally by surprise. Most of us, if we have a level head on our shoulders, do not do our work with the thought that we will some day be presented with a major award because of it. Especially those of us in the world of public service and nonprofits, where dedication to the greater good is a primary motive, even though we are not immune to thinking about raises and promotions, which, after all, may enable us to be more effective in what we do.
Consequently, when the Association of State Floodplain Managers (ASFPM) asked me to attend the annual ASFPM conference in Phoenix last week (June 17-21), I naively accepted the rationale that, since they had recently contracted with me as an independent consultant to lead the production of a Planning Advisory Service Report on climate resilience and capital improvements planning, under a Regional Coastal Resilience grant from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), they needed me there to discuss the project. I had helped write the grant three years ago while still leading the Hazards Planning Center at the American Planning Association (APA), which became the major partner to ASFPM in conducting the three-year project. Although I retired from that position a little more than a year ago, there was a great deal of logic in bringing me back to see at least that part of the project to a successful conclusion.
There was only one problem in Phoenix. No one seemed all that concerned about spending time talking to me about the NOAA project. I was certainly learning a great deal by listening to presentations, and I certainly enjoyed networking with colleagues at receptions and in hallways at the Phoenix Convention Center, but the question was bugging me: Why did they really want me out here?
On Thursday morning, June 21, before the morning plenary began in the Ballroom, I approached David Conrad and Larry Larson at a front table after initially parking my belongings at another table further back. David Conrad was once with the National Wildlife Federation and wrote a path-breaking report following the 1993 Midwest floods. Larry is the former executive director of ASFPM and now a policy advisor working with current executive director Chad Berginnis. Both are prominent in the field of floodplain management.
I patted David on the shoulder and with self-effacing humor said, “I used to sit at the front table before I retired from APA, but now I’m nobody anymore.” They chuckled, and ASFPM’s public information officer, Michele Mihalovich, said from across the table, “Jim, you’ll never be nobody.” We all laughed, David invited me to join them, and I moved to the front table for the plenary. All good for a laugh. Afterwards, Larry made a point of asking me to find him at a front table, off to the side, for the awards luncheon at noon. Still clueless, I assumed he was simply being friendly but honored his request when the time came.
Lunch was served, and Doug Plasencia, president of the ASFPM Foundation, and Diane Brown, retiring from her post as outreach and events manager at ASFPM after 35 years of excellent service, introduced award recipients and their achievements one at a time, with images on the screen, and each winner stood with presenters for a photo. Interesting, I thought, in considering the various prizes, but routine. I was happy for the winners, some of whom I knew. Almost every national professional organization does such things. Meanwhile, I ate my salad, the roast beef entrée, and the dessert. In a little while, it would all be over, and we would move on to an afternoon of presentations and discussions in a variety of concurrent sessions. I flipped through the program to see what looked interesting.
Finally, Diane Brown began to describe the winner of the highest honor ASFPM bestows, the Goddard-White Award, described thus on the website:
“The Goddard-White Award is named in honor of the contributions made to floodplain management by Gilbert White (1911- 2006) and Jim Goddard (1906-1994). This award is given by ASFPM to individuals who have had a national impact carrying forward the goals and objectives of floodplain management. It is an indication of the level of esteem the association holds for the two namesakes as well as the recipients and is ASFPM’s highest award. It is not necessarily presented every year.”
I’m not sure because one does not time such things. I believe it took about 30 seconds of Diane’s narration of the story behind this year’s award before it suddenly dawned on me that I was the person they were talking about. I had never spent one minute before that contemplating this specific award or how I might have anything to do with it. The revelation that I was a recipient struck me like a lightning bolt. Larry was looking toward me, and I pointed to myself silently as if so say, “Moi?” He kept his Cheshire cat smile and waited for the emcees to invite me forward. Larry, by the way, was in 1985 the very first recipient of this honor. He had known all along precisely what was coming. Diane invited me to the podium to say a few words. A few tears started to run down my cheeks, so I struggled to get them under control. At the podium, Diane asked, “Are you okay to talk?” I nodded yes.
I cannot repeat verbatim what I said because it was all spontaneous, but I know that I began by saying that we in the hazards world are “supposed to be prepared. I am not. You caught me off guard.” I took the crowd on a two-minute tour of what we had achieved together in the partnership of recent years that I helped construct between ASFPM and APA, and said, “Eventually, you look back and ask, ‘Did we do all that?’” I then explained that it was not just me. I had learned a great deal over the years from many other people, that big achievements require collective effort. And I thanked everyone for this high honor before stepping over to the curtain for a photograph that you see above.
I checked later and found that only 24 people have received this award, including former NOAA Coastal Services Center administrator Margaret Davidson, a truly memorable individual, U.S. Rep. Earl Blumenauer of Oregon, a perennial warrior for better disaster legislation, and French Wetmore, who helped create the Federal Emergency Management Agency’s Community Rating System for the National Flood Insurance Program. All I can say is, Wow. What a band of high achievers and visionaries I have apparently joined.
It is hard to top such an honor, except in one way: It is important not to rest on these laurels, but to continue to contribute, to encourage others to find their passion, and to remain an effective voice for positive change. I hope I am doing that and can remain part of the action for many years to come. Thanks, ASFPM. I hope I can prove you right.
Jim Schwab