The American Planning Association has just posted today this article I wrote for its APA blog: https://www.planning.org/blog/blogpost/9111027/.
Jim Schwab

The American Planning Association has just posted today this article I wrote for its APA blog: https://www.planning.org/blog/blogpost/9111027/.
Jim Schwab
One of the ongoing, perhaps permanent, struggles in public policy in a democracy like ours involves finding a balance between enabling private sector opportunities and protecting both the public interest and the public purse. Depending on their philosophies and perspectives, people will naturally draw those lines in different places on different issues. But sometimes it is perfectly clear when the public interest is about to suffer a hit. Currently, one of those possibilities involves the fate of the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP).
On April 28, the U.S. House of Representatives passed HR 2901, a bill that seeks to make it easier for private companies to write private flood insurance policies that can take the place of those provided by the NFIP. The NFIP was created under the National Flood Insurance Act of 1968 to provide insurance that was then largely unavailable on the private market, but it also set in motion the creation of a federal regulatory program that has established standards for floodplain management in more than 22,000 communities nationwide. Many of those communities, particularly smaller ones, have no other meaningful land-use regulations, unlike bigger cities and suburbs and communities in states that mandate planning, which typically have comprehensive plans, zoning ordinances, and subdivision regulations. The reason is that federal flood insurance is made available only in communities that have adopted the minimum standards of the NFIP, which seek to achieve flood loss reduction, thus reducing the damages from flooding and the resultant payouts under flood policies.
It makes perfect sense. There is no good reason for the federal government to insure properties against flood losses without making some attempt to minimize those losses through sensible land-use measures. Private casualty insurers certainly make attempts within their means to reduce losses from other types of accidents and disasters. Why not the federal government?
There is nothing inherently wrong with expanding opportunities for private flood insurance coverage. But there are serious issues with HR 2901, and the Association of State Floodplain Managers (ASFPM), an organization with which I work closely as manager of the Hazards Planning Center at the American Planning Association (APA), has mounted an alert among its members to urge U.S. Senators to take time to examine the bill closely before taking any action this fall. It has also addressed the issue earlier in testimony before the Senate Committee on Small Business and Entrepreneurship. The Senate is in recess until September 6. ASFPM would ideally prefer that Congress defer action until next year, when the NFIP is due for reauthorization in any case, in order to consider the unintended consequences of the House bill in line with the larger objectives of the NFIP. APA is in support of the ASFPM effort in this regard.
The NFIP has evolved for nearly half a century with numerous revisions and reforms over time. Like any such program, it has needed to evolve in response to new lessons and changing circumstances. Some of the most significant lessons of the past came from the 1993 Midwest floods, which spawned reforms a year later. Among numerous changes that year was modification of policies to include Increased Cost of Compliance, which allows policies to pay for building improvements in response to higher local building standards, for example, by requiring elevation of buildings above the Base Flood Elevation, which is basically the height of the 100-year, or one percent chance annual flood, as mapped on the NFIP’s Flood Insurance Rate Maps. It is in the public interest to facilitate the capacity of communities to upgrade such codes over time as new lessons are learned, and to make it financially feasible for policy owners to comply with those new standards when rebuilding after a flood.
To be sure, these maps have never been perfect indicators of flood risk, though they are getting better with current digitization initiatives. Still, only about 1.2 million miles of shoreline and riverfront have been mapped, while more than 2/3 of the miles of the nation’s waterways are not. Most of the latter are small creeks and streams outside developed areas, which clearly have always been the priority. But it also means that development can occur in less developed areas without requirements to meet standards that only apply to mapped floodplains—unless a local jurisdiction is proactive enough to require developers to map such areas before new subdivisions or other development can be considered. Mostly, that is not the case.
So what is at issue with HR 2901? For one thing, NFIP policies include a policy fee that helps underwrite the cost of all this mapping, including updates and corrections over time. It is an ongoing process in part because floodplains are not static geographic entities. They expand or contract with the impact of our development practices, which affect the amount of impervious surface in urbanized areas, which affect how stormwater and other runoff is absorbed into the ground or directed downstream. Further, according the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), about 40 percent of flood-related losses occur outside mapped floodplains. Why? Because not all floodplains are adequately mapped or as yet mapped at all, and because flooding can occur outside and beyond the 100-year floodplain, and often does. We have Certified Floodplain Managers these days because this is, in fact, a complex and technical subject.
The problem with not including policy fees in the private policies is that the burden of financing this public good of mapping floodplains and maintaining a mountain of data about flood hazards falls to those NFIP policyholders who are paying for it, or to the American taxpayer when Congress allocates money directly for the purpose. The fee also supports flood hazard reduction efforts under FEMA’s Flood Mitigation Assistance program. That creates an inequity in favor of private flood insurance. But that is not all. Although federal financial regulators have had authority to establish policies concerning what provisions in a private policy would make them acceptable as an alternative to an NFIP policy, they have not acted. FEMA legal advisors, for whatever reason, decided in 2013 they did not have the authority to issue guidance. So the House bill assigned this responsibility to state insurance commissioners while prescribing that lenders and federal bank regulators “shall accept” the standards laid out by the states. It would be small surprise to anyone knowledgeable in this field to discover that state regulation in most cases is likely to be minimal and limited. The only required equivalency in the House bill will deal with the coverage amount, which may result in much smaller private premiums with high deductibles that may be superficially attractive—until homeowners with large deductibles find they lack the resources to rebuild and just walk away, quite possibly leaving communities and the federal government holding the bag for addressing the problems of neighborhoods with spotty redevelopment and blighted properties.
All of this, at the very least, deserves some serious debate before the Senate accepts the House version, but proponents have been seeking to fast-track the Senate bill (S 1679) under a process known as Unanimous Consent. However, if enough Senators hear enough complaints, fast-track may become a less attractive option. And, as noted earlier, there are good reasons to delay this discussion and take it up as part of the NFIP reauthorization next year, so that both Senators and the public can begin to understand the full implications of what has been proposed.
In no way would this be a death knell for private flood insurance. One problem the bill deals with in two useful paragraphs is to allow the private policies to be considered “portable” for the purpose of maintaining an unbroken record of coverage for a property if the owner switches between public and private insurance. That has not been the case but is not hard to fix. ASFPM notes that there has been a doubling in the last couple of years of companies offering private insurance. In other words, the expansion of private flood insurance is already happening. There is no reason to create a whole class of private policies that are not truly equivalent to those of the NFIP and, in the process, undermine the public goods produced by the NFIP and quite likely, increase the number of property owners seeking disaster assistance after discovering they are inadequately covered.
Flood insurance policy has already entered a volatile period that began with the Biggert-Waters Flood Insurance Reform Act of 2012, passed just a few months before Hurricane Sandy. While trying to place older, subsidized policies on a path to actuarially justifiable rates, it triggered a political backlash when rates began to soar after the impact of Hurricane Sandy. By 2014, Congress somewhat reversed course but has left unresolved a number of issues concerning how previously subsidized policyholders could afford their now escalating premiums as Congress sought to reconcile affordability with a desire to place the NFIP on a fiscally sound footing. It is a thorny issue at best, and we surely have not heard the end of it. The simple fact is that large numbers of older, poorly protected properties in or near floodplains are likely to continue to generate flood losses into the future.
We already have a flood insurance program that is $23 billion in debt to the U.S. Treasury because of Hurricanes Katrina and Sandy, which overrode assumptions that the NFIP would largely insure garden-variety disasters. Next year’s reauthorization could sensibly forgive this debt in order to begin to place the NFIP back on a fiscally sound footing, but not with the approaches in HR 2901. We need to strengthen, not weaken, a system that at least drives toward stronger floodplain management and flood mitigation. We need to get this train moving again in the right direction. Congress needs generally to be more productive than it has been in recent years, but it also needs to put more thought into this particular issue and act in less haste. The alternative is to continue to generate a long train of unintended consequences and later ask what happened and why.
Jim Schwab
Chicago is already quite rich in parks and tourist attractions. What can it add downtown?
In the past, I have written about the 606 Trail in Chicago, which is experiencing its first anniversary after opening a year ago. Despite some of its well-known challenges and problems, Chicago remains a city of quality destinations. Navy Pier, now a century old, just unveiled its redesign last month, including a new 200-foot Ferris wheel, and has been the top tourist attraction in Illinois. Millennium Park has few peers among downtown urban parks and has also been a second magnet for visitors since opening in 2004, ranking only behind Navy Pier.
But below the bridges and viaducts, down near the water’s edge, another jewel is nearing completion along the Chicago River—the Riverwalk. On June 2, I joined a tour sponsored by both the American Planning Association Illinois Chapter and the American Society of Landscape Architects Illinois Chapter and listened to an explanation of both completed and upcoming changes.
Chicago has no shortage of websites and museums devoted to its own urban history, which I won’t even try to summarize here. Suffice it to say that, when Haitian-French explorer-trader Jean Baptiste du Sable first encountered Potawatomi Indians (one of whom he married) at the shore of Lake Michigan in 1790, the Chicago River was still an indolent waterway barely crossing the sandbars to empty into the lake. In a little over 200 years, it has become home to one of the world’s largest cities, with all the pollution and navigation over two centuries that one might expect. In the 1890s, amid the city’s rapid industrial expansion, engineering reversed its flow away from the lake to the Mississippi River watershed, in large part to spare Chicagoans the pollution of their beaches and water supply that came with using the river as an open sewer. The river itself was not a place where you wanted to spend time unless you were in a boat, and even that was questionable. More than 800 picnickers died when the Eastland tipped over at the water’s edge in 1915. At street level on Wacker Drive, a plaque memorializes that notorious incident.
But times change, and in the 21st century, the Chicago River is once again a civic asset to which significant attention—and investment—are being paid. Over the last ten years, the first two phases of a rebuilding project have come to fruition, producing a Riverwalk that now extends on the south side of the main branch from Michigan Avenue west to LaSalle St. A third phase will extend the Riverwalk further west to the juncture of the North and South Branches. Even the term “main branch” may seem a little puzzling to non-natives because it extends only about one mile. Most of the length of the Chicago River is in the two branches, but the whole river in either direction is less than 20 miles. The Lake Michigan watershed in this instance barely reaches beyond the city and rises only about 20 feet above the lakeshore. Beyond that, you are in one of the sub-watersheds of the vast Mississippi River valley. Most people would never notice they had crossed this boundary if a sign did not tell them. The Continental Divide, this is not.
However, the controlled nature of the river and the short reach of the main branch make the creation of a downtown Riverwalk far more manageable and the experience of walking it thoroughly enjoyable. The firms of Jacobs/Ryan Associates, Sasaki Associates (with whom I have collaborated on disaster recovery issues), and Ross Barney Architects, involved in the design and engineering, have produced an experience that unfolds in “rooms” as one moves in either direction along the river, bringing users close to the water while allowing the occasional flood to muddy some steps without much damage beyond washing down the mud the next day. Phase 1redesigned and rebuilt an existing path between Michigan Avenue and the lake, an area popular with tourists as a loading zone below the stairs from Michigan Avenue down to the riverfront for tour boats. It then extended that two blocks westward to State  Street and includes the Chicago Veterans’ Memorial Plaza, opened in 2006. One of its nice touches is a series of concrete stairs more suitable for lunch or relaxation than for climbing. It is a dignified but welcoming setting in keeping with its purpose. In Phase I, the idea began to emerge of adding river-level sidewalks that allow visitors to move from block to block without going up to street level and back down again, although some of these obviously had to intrude from the existing river’s edge into the waterway, and thus involved some negotiation among agencies responsible for navigation and safety, given the mix of water traffic still traversing the Chicago River. Congress also had to act to provide permission to allow building 25 feet into the river to create the necessary width for the new Riverwalk.
Street and includes the Chicago Veterans’ Memorial Plaza, opened in 2006. One of its nice touches is a series of concrete stairs more suitable for lunch or relaxation than for climbing. It is a dignified but welcoming setting in keeping with its purpose. In Phase I, the idea began to emerge of adding river-level sidewalks that allow visitors to move from block to block without going up to street level and back down again, although some of these obviously had to intrude from the existing river’s edge into the waterway, and thus involved some negotiation among agencies responsible for navigation and safety, given the mix of water traffic still traversing the Chicago River. Congress also had to act to provide permission to allow building 25 feet into the river to create the necessary width for the new Riverwalk.
 What has emerged in Phase II is the creation of the rooms: Marina, Cove, and River Theater, extending from State Street west. The first is opposite Marina City, occasionally nicknamed the “Corncob Towers” because of their design, and permits docking by river boats and lounging by pedestrians. The Cove, in contrast, is a favorite stopping point for kayaks and canoes, which provide a rich source of aquatic exercise for sports enthusiasts. The River Theater changes the nature of the experience yet again with the appearance of a riverside amphitheater, using a low-slope path woven into climbing stairs that can also double as points of relaxation for hikers. The theater, for the most part, is the activity on the river itself, although one can imagine a waterborne performance someday floating before the viewers. Most of this opened for public use just a year ago.
What has emerged in Phase II is the creation of the rooms: Marina, Cove, and River Theater, extending from State Street west. The first is opposite Marina City, occasionally nicknamed the “Corncob Towers” because of their design, and permits docking by river boats and lounging by pedestrians. The Cove, in contrast, is a favorite stopping point for kayaks and canoes, which provide a rich source of aquatic exercise for sports enthusiasts. The River Theater changes the nature of the experience yet again with the appearance of a riverside amphitheater, using a low-slope path woven into climbing stairs that can also double as points of relaxation for hikers. The theater, for the most part, is the activity on the river itself, although one can imagine a waterborne performance someday floating before the viewers. Most of this opened for public use just a year ago.
Phase III is adding a water plaza at the river’s edge; the Jetty, which places a series of floating gardens along the river edge that allow people to learn about river ecology and native plants, and the Boardwalk, providing an accessible walkway connecting to Lake Street. Although currently inaccessible at river level, one can view the construction on the final phase from street level. We were told the project will be completed by this fall.

O’Brien’s is one of the existing restaurants, along with City Winery, that provide refreshment along the route.
It is one thing to traverse this path with a crowd from a mobile workshop in the late afternoon. Not only does a crowd make a difference, so does timing. I returned the following morning, since my CTA Blue Line commute takes me to the Clark & Lake station. Instead of remaining on Lake Street, I walked to Wacker Drive and descended the stairway again, this time walking in the cool of the morning by myself at 8 a.m. Not that I was alone. The path was already being filled with pedestrians like me, and joggers, and even an occasional bicyclist, so I had to pay attention to those around me as I repeatedly set my camera to shoot many of the photos included here. Heat varies, of course, throughout the summer day, but one pleasant, enduring feature is the cool breeze off the water. In the morning, as well, the restaurants are not yet open, making for a slightly more solitary experience, which even a confirmed extrovert like me can enjoy in contrast to the crowds that by late afternoon are now finding their way to the
new bars and restaurants that are now exploiting the popularity of the Riverwalk, as intended, with more coming as the project moves along. The opportunity to sit outdoors at river level and enjoy snacks or dinner and drinks can be very pleasant, and very different from the usual experience high above on the city streets. I expect that most of these establishments will do quite well. I intend to enjoy some of them myself, with friends in tow.
Jim Schwab
The subtitle to this headline for many people might be: Who Cares? As a term of art, green infrastructure may be popular with landscape architects, civil engineers, and urban planners, among a few other allied professions, but it does not often mean much to the average person. Many people may struggle to define infrastructure even without the word green in front of it.
Infrastructure generally refers to those modern systems, such as roads, bridges, and utility grids that allow our cities and regions to function effectively. Recognizing that the value of infrastructure lies in the services it provides, green infrastructure has been distinguished from traditional gray infrastructure by focusing on the use of natural systems, such as wetlands and urban forests, to protect or enhance environmental quality by filtering air pollution, mitigating stormwater runoff, and reducing flooding. It stands to reason that such natural systems are most likely to provide such “ecosystem services” well when we respect and preserve their natural integrity. It also stands to reason that, to the degree that such systems face threats from urban sprawl and urbanization, their ability to perform those services for human populations is diminished. To say that development has often helped to kill the goose that laid the environmental golden egg is to state the obvious, no matter how many people want to avoid that truth. That does not mean that our cities cannot or should not grow and develop. It does mean that, using the best available natural science, we need to get much smarter about how it happens if we want to live in healthy communities.
I mention this because, as part of the American Planning Association staff pursuing such issues, I spent three days in Washington, D.C., last week at a symposium we hosted with U.S. Forest Service sponsorship on “Regional Green Infrastructure at the Landscape Scale.” We were joined by about two dozen seasoned experts not only from the Forest Service and APA, but from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, several national nonprofits, and others to sort through the issues impeding better planning for green infrastructure. We explored major hazard-related issues such as wildfires, flooding, and coastal storms and how green infrastructure can or should function in relation to them.
This matters because there are huge costs associated with the way we choose to develop. There can also be huge benefits. Whether the ultimate ledger in any particular region is positive or negative is largely dependent on the approach we choose, and that is heavily dependent on how broadly or narrowly we view our responsibilities. Historically, in America, we have been rather myopic about the damage we have done to our environment, but our perspective has become more comprehensive over time, starting with the conservation movement in the late 1800s. But today, as always, there are undercurrents of more myopic attitudes and impatience with the more deliberate and thoughtful calculations a more long-term view requires. There is also the simple fact that understanding issues like climate change requires some degree of scientific literacy, something that is missing too often even in some presidential candidates.
But it helps to drill down to specific situations to get a firm sense of consequences. For instance, the Forest Service budget is literally (and figuratively) being burned away by the steadily and rapidly increasing costs of fighting wildfires. That is in large part because the average annual number of acres burned has essentially tripled since 1990, from under 2 million then to about 6 million now. As recently as 1995, 16 percent of the agency’s budget went to suppressing wildfires. Every dollar spent on wildfires is a dollar removed from more long-term programs like conservation and forest management. By 2015, this figure has risen to 52 percent, and is projected to consume two-thirds of the agency’s budget by 2025. Clearly, something has to give in this situation, and in the present political situation, it is unlikely to be an expansion of the Forest Service budget. At some point, a reckoning with the causes of this problem will have to occur.
What are those causes? Quite simply, one is a huge expansion in the number of homes built in what is known as the wildland-urban interface (WUI), defined as those areas where development is either mixed into, interfaces with, or surrounds forest areas that are vulnerable to wildfire. The problem with this is that every new home in the WUI complicates the firefighters’ task, putting growing numbers of these brave professionals at risk. Every year, a number of them lose their lives trying to protect people and property. In an area without such development, wildfires can do what they have done for millennia prior to human settlement—burn themselves out. Instead, a century of aggressive fire suppression has allowed western forests, in particular, to become denser and thus prone to more intense fires than used to occur. The homes themselves actually represent far greater densities of combustible material than the forest itself; thus fires burning homes are exacerbated by increased fuel loads. In addition, prescribed fire, a technique used to reduce underbrush in order to reduce fire intensity, becomes more difficult in proximity to extensive residential development. A prescribed fire that spun out of control was the cause of the infamous Los Alamos, New Mexico, wildfire in 2000. The entire situation becomes highly problematic without strong political leadership toward solutions.
At the same time, denial of climate change or even reluctance to broach the subject does not help, either. It compounds the difficulty of conducting an informed dialogue at a time when increased heat and drought are likely to fuel even more wildfires of greater intensity. The recent major wildfire around Fort McMurray, Alberta, displacing thousands of people, may be a harbinger of things to come.
That is just one sample of the issues we need to confront through a larger lens on the value of large-scale green infrastructure and regional cooperation to achieve positive environmental results that also affect issues like water quality and downstream flooding. Because we could produce an entire book on this issue—and the suggestion has in fact been made that we do so—I will not even attempt here to lay out the entire thesis. Rather, it may be useful to point readers to some resources that I have found useful in recent weeks in the context of writing for another project on green infrastructure strategies. Most of these are relatively brief reports rather than full-length books, enough to give most readers access to the basics, as well as references to longer works for those so inclined.
On the subject of water and development in private forests, a Forests on the Edge report, Private Forests, Housing Growth, and Water Supply is a good starting point for discussion. Because planning to achieve effective conservation at a landscape scale requires collaboration among numerous partners, an older (2006) Forest Service report, Cooperating Across Boundaries: Partnerships to Conserve Open Space in Rural America, may also be useful. With regard to wildfires, a recent presentation at a White House event by Ray Rasker, executive director of Headwaters Economics, a firm that has specialized in this area, may also be useful for its laser focus on trends and solutions with regard to development in the wildland-urban interface and the need for effective, knowledgeable local planning in areas affected by the problem. But I would be remiss if I did not bring readers’ attention back to a 2005 APA product of which I was co-author with Stuart Meck: Planning for Wildfires. It could probably use some updating by now, but every one of our central points, I believe, remains valid.
Happy reading to all!
Jim Schwab

Sylvia Vargas and Ben Carlisle present FAICP medallion and certificate in Phoenix. Photo by Joe Szurszewski; copyright by American Planning Association.
Sometimes we find ourselves on a journey whose significance is bigger than the meaning for our own lives alone. In fact, if we are lucky, we come to realize that we can make at least some part of our lives much bigger than ourselves. Two weeks ago, while in Phoenix, being inducted into the College of Fellows of the American Institute of Certified Planners (AICP), one of the highest honors in the profession of urban planning, it became very apparent to me that I was not accepting this honor just for myself. I was also doing it for hundreds of other planners, if not thousands, who have incorporated disaster recovery and hazard mitigation priorities into their careers as essential parts of the ethical duty of planners to help promote public safety. Collectively, our work saves lives, reduces property damage, and reduces many of the negative impacts of human activities on the planetary environment.
Before I go farther in discussing those impacts, let me provide some context for the majority of readers who are not professional planners. AICP is a designation currently held by at least 15,000 professionals who have taken a certification exam, eligibility for which is based on a combination of education and experience. Most common these days as a starting point is a Master’s degree in urban planning, but there are other entry points, and there are undergraduate degrees in planning as well. AICP members, who are also members of the American Planning Association (APA), which has about 38,000 members, must maintain their status through a minimum of 32 hours of continuing education every two years, including 1.5 hours each of legal and ethical training. Only after a minimum of 15 years in AICP are planners eligible for consideration, through a rigorous review of their accomplishments and biography, for acceptance as fellows (FAICP). Only about 500 people have ever been inducted as fellows, including 61 in this year’s biennial ceremony, the largest group to date. I had the honor of being included in the class of 2016.
The very formal ceremony introduces each new fellow individually in alphabetical order while a member of the AICP review committee reads a 100-word summary of his or her achievements, during which the fellow receives a pin, a bemedaled ribbon, and certificate. Mine described my work as “pivotal” in incorporating natural hazards into the routine work of urban planners. That pivotal work is the point of my discussion that follows.
I did not start my work in urban planning with any focus on disasters, except perhaps the industrial variety. I did have an intense focus 30 years ago on environmental planning and wrote about issues like farmland preservation, Superfund, waste disposal, and other aspects of environmental protection. My first two books focused, in order, on the farm credit crisis of the 1980s and the environmental justice movement, the latter published by Sierra Club Books. I have joked in recent years, sometimes in public presentations, that even with that environmental focus in my academic training at the University of Iowa in urban and regional planning, I don’t recall ever hearing the words “flood,” “hazard,” or “disaster” once in all my classes. But I did hear about wetlands, air quality, water quality, and similar concerns. Frankly, in the early 1980s, natural hazards were simply not on the radar screen as a primary professional concern for any but a mere handful of planners. Even the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) came into being only in 1979, and these issues were seen largely as the purview of emergency managers. There certainly was no significant subdiscipline within planning devoted to hazards.
It was 1992 when Bill Klein, then the research director for APA, asked me to take over project management for an upcoming cooperative agreement with FEMA to examine planning for post-disaster recovery. As a preliminary step to this work, he sent me on a trip to south Florida for the APA Florida Chapter conference in October 1992 in Miami following Hurricane Andrew. Two aspects of that trip made a lasting impression. First was the keynote delivered by Bob Sheets, then the director of the National Hurricane Center. At one point, he showed a slide on the huge screen at the front end of the ballroom. It was an aerial photo of damage on two sides of a highway, with one side showing only modest damage and the other massive damage with roofs torn off and homes destroyed. There was no differential in wind patterns, he said, that could explain such differences at such small distances. The only plausible explanation, he insisted, lay in differences in the quality of enforcement of building codes. Florida then had stricter building codes than the rest of the nation for wind resistance, but they only mattered if code enforcement was consistent. Here, it was clear to me, was a problem directly related to development regulations. The second involved a field trip aboard several buses for interested planners to south Dade County. At one point I saw that the roof of a shopping center had been peeled off by the winds. It nearly took my breath away. Then our buses got caught in a traffic jam at the end of the afternoon. The cause was a long line of trucks hauling storm debris to landfills. This was already two months after Andrew.
Under the agreement, we didn’t start work on the project until October 1, 1993. In the meantime, floods had swept the Upper Midwest, making parts or all of nine states presidential disaster declaration zones. I decided to jump the gun on our start date and visit Iowa while it still was under water. Local planning departments in Iowa City and Des Moines cooperated in showing me their cities and sharing what had happened. It turned out that I was undertaking this project, in which I engaged several veteran planners to help write case studies and other material, at the beginning of America’s first big decade of disasters. (The next was even bigger.) In 1994, the Northridge earthquake struck the Los Angeles area. In 1996, Hurricane Fran struck North Carolina, followed by Hurricane Floyd in 1999. In the meantime, not only had our report, Planning for Post-Disaster Recovery and Reconstruction, been published in 1998, but so was another report of which I was the sole author: Planning and Zoning for Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations. Floyd left much of eastern North Carolina, liberally sprinkled with poultry and hog feedlots as a result of regulatory exemptions, devastated, with hundreds of thousands of animal carcasses floating downstream. Eventually, they were burned in mobile incinerators introduced by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Suddenly, it became apparent to me that the environmental concerns aroused by such operations and the impacts of natural disasters were thoroughly intermingled. Bad public policy was exacerbating the impact of disasters like hurricanes and floods.
At this point, I need to make clear how low the level of engagement was back then between professional planners and disaster issues. In 1995, the APA National Planning Conference, which in recent years has typically attracted about 5,000 registrants, included two sessions related to disasters, at which the total attendance was 73 people. Disasters were anything but the topic du jour. Yet the events of that decade made clear, at least to me, that something had to change in that regard.
What I did not anticipate, based on past experience, was how quickly that would happen. For one thing, the Planning Advisory Service (PAS) Report grew on people and became a classic in the planning field. By 2005, after Hurricane Katrina, APA published a new edition, and FEMA made boxes of them readily available in the Gulf Coast, with planners like Stephen Villavaso, then the president of APA’s Louisiana chapter, voluntarily driving through stricken towns and passing out copies to local officials. In the meantime, I had worked on several other hazard-related projects addressing planning for landslides and wildfires and providing training on local hazard mitigation planning, among other efforts. After the APA conference in New Orleans in 2001, a group formed and continued to meet over dinner at every subsequent conference that billed itself as the “Disaster Planners Dinner,” an event that has become the subject of some legends among its veterans. The growing contingent of planners taking hazards seriously as a focus of their professional responsibilities was growing quickly and steadily.
Hurricane Katrina, more than any other event, added a powerful new element to the public discussion. It made crystal clear to the national news media that planning mattered in relation to disasters, and because of that perception, they called APA. Paul Farmer, then the CEO and executive director, and I shared those calls, and I logged no fewer than 40 major interviews in the two months following the event in late August 2005. I stressed that disasters involve the collision of the built environment with utterly natural events, and the resulting damage is not an “act of God” but the outcome of human decisions on what we build, where we build it, and how we build it. Planners have the responsibility to explain the consequences of those choices to communities and their elected officials during the development process, and those choices sometimes have huge social justice impacts. Katrina cost more than 1,800 lives on the Gulf Coast, most of them involving the poor and the physically disadvantaged. Better planning thus became a moral imperative. Making that perception stick produced a sea change in public understanding of the high stakes involved.
That afforded me considerable leverage to win funding for new projects with FEMA and other entities, most notably including the 2010 publication of Hazard Mitigation: Integrating Best Practices into Planning, a PAS Report that argued strongly for making hazard mitigation an essential element of all aspects of local planning practice, from visioning to comprehensive planning to policy implementation tools like zoning and subdivision regulations. Now the focus of a growing amount of federal and state guidance in this arena, that report was followed in 2014 with a massive update and revision of the post-disaster report, Planning for Post-Disaster Recovery: Next Generation, which dissected the whole process of long-term community recovery from disasters and argued fervently for pre-disaster planning to set the stage for effective recovery and resilience after an event. Those efforts came under the umbrella of the Hazards Planning Center (HPC), created by APA in 2008 along with two other centers as part of the National Centers for Planning. I have been the manager since HPC’s inception, and I was happy. We had succeeded in institutionalizing within the profession what had once been treated as a marginal concern of planners.
Along the way, that dinner group grew, attracting dozens of attendees by the end of the decade, and becoming large enough and attracting enough petition signatures to become APA’s newest membership division in 2015, the Hazard Mitigation and Disaster Recovery Planning Division. They now meet as such during the APA conferences. They are no longer an informal group. They are official and at last count had at least 250 paid members. But the interest is far larger. Remember those numbers from the 1995 APA conference? In Seattle at the 2015 APA conference, almost 3,000 people attended 23 different sessions related to climate change and natural hazards. I was the opening speaker for the very first session in the climate track, and the room was full. There was an overflow crowd in the hall outside. Hazards and climate change adaptation had arrived as a primary concern of planners. A growing number of graduate schools of planning, including the University of Iowa, where I have been adjunct faculty since 2008, now include curricula on such topics.
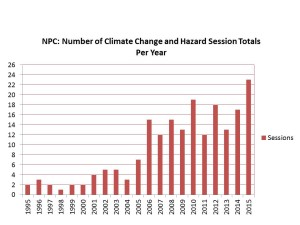
This bar graph and the one below were developed last year for a presentation I did in July 2015 at the opening plenary of the 40th annual Natural Hazards Workshop, in Broomfield, Colorado.
I want to state that, although I often had only one intern working with me at APA, I have never been a one-man show. On most of those projects, I involved colleagues outside the APA staff as expert contributors and invited many more to symposia to help define issues. Those APA sessions attract numerous speakers with all sorts of valuable experience and expertise to share. This is a movement, and I have simply been lucky to have the opportunity to drive the train within the APA framework as the head of the Center.

The night after the FAICP induction, at their division reception, members of the new APA division jokingly award me an “F” to go with my AICP. Alongside me is Barry Hokanson, HMDR chairman.
So let me take this story back to that moment two weeks ago when I walked on stage and accepted induction into FAICP. Before, during, and after that event, I received congratulations from many colleagues intensely interested in hazards planning, and I realized I was not simply accepting this honor for myself. My achievement was theirs too, and was literally impossible without them.
“You’ve gone from fringe to mainstream,” my colleague Jason Jordan told me the opening night of the Phoenix conference. He ought to know. Jason is the experienced governmental affairs director for APA and has a keen sense of the trends in planning and of government policy toward planning. But in order for his statement to be true, one important thing had to happen: Lots of other planners had to climb aboard that train for the journey. My success in winning this honor was symbolic for them, in that it served to validate the value of their commitment. I did not get there alone. A growing army of planners who care about public safety and community resilience helped make it happen, and I shall always be grateful—for them as well as for myself.
Jim Schwab

Occasionally, I have used this blog to link to American Planning Association blog posts that I think some readers may find important. That is the case here: At the APA blog, I provide a brief introduction to a wonderful new resource for communities on a variety of water-related issues, ranging from not enough (drought), to too much (flooding), to not good enough (water quality), and other aspects and manifestations of the numerous ways in which water influences our lives and the way we build and move around. I am pleased to have played a role on behalf of APA in helping vet and shape this new resource.
What is it? The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration has created a Water Resources Dashboard for those needing timely information on water from a number of perspectives. Check it out. It is a great example of how a user-friendly federal agency can provide a great service to citizens and communities and raise the level of scientific awareness generally.
Photo from NOAA Water Resources Dashboard site
Jim Schwab
Across the United States of America, about one in five people live under the rules and structures of some sort of private association that governs common property interests. These can be condominium associations, homeowners associations, or similar entities that are somehow responsible for levying fees and maintaining communal property. To degrees they often may not realize, the residents are thus controlled and constrained by the decisions these associations make, which often may concern themselves with details that a local government would not even consider, such as the color of aluminum siding, allowable holiday decorations, and other matters with minor impacts on the quality of life. Many homeowners associations are established by developers at the time they get permits to create a new subdivision. In some states, local governments are happy to offload responsibility for infrastructure maintenance, such as private roads, onto these associations while coveting the property taxes they will still pay.
The implications of all this were brought to my attention in the past week or two by Chad Berginnis, the executive director of the Association of State Floodplain Managers (ASFPM). He has been working with me on material for a future report we plan to publish at the American Planning Association on subdivision design as it relates to areas with flood hazards. The issue that concerned him as he wrote a chapter on subdivision standards for local governments, which have the primary responsibility for permitting new development, is how well these private owner associations can sustain over time the financial responsibilities for infrastructure designed to protect their properties from disaster, most notably but not exclusively, flooding.
Among the items that have come to my attention is a paper by two California attorneys, Tyler P. Berding and Steven S. Weil, disturbingly titled, “Disaster! No Reserves. No Insurance. What’s Left if a Natural Disaster Destroys a Community Association?” They begin with a cautionary tale about the Bethel Island Municipal Improvement District, actually a California special district, not a homeowners association. Its mission is to maintain and improve the levees that surround the Sacramento Delta island of 2,500 residents, where the interior is seven to 15 feet below sea level. To say that their survival depends on well-maintained levees is no exaggeration. Moreover, in that part of California, the levees are subject to collapse from earthquake shaking as well as from overtopping in a flood. I have some idea of their peril because four years ago, a representative of the California Department of Water Resources (DWR) took me on a six-hour guided tour of the levee system in the delta area, plying me with a number of the background studies by DWR of the overall situation. There are hundreds of such islands throughout the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta, many used for agriculture, and some developed. In their 2012 article, produced about the time of that tour, Berding and Weil note, “But the district is broke.” Voters “soundly” rejected a 2010 parcel tax measure to fund improvements, and much of the district staff was laid off. The levees were deteriorating, to some extent “suffering damage by beavers and rodents.”
It is disturbingly easy for homeowners association or other private association board members to take their eyes off the ball of maintaining adequate reserves and resources to address dangers that seem less than imminent, and even to forget why they are responsible for collecting assessments in the first place. And it is even easier for residents who must approve some of those assessments to lack meaningful knowledge of the consequences of either depleting or failing to maintain adequate reserves for unfortunate natural events like floods, earthquakes, or other disasters. Once they begin sliding down that slippery slope of amnesia and unawareness, it is not long before they have put a good deal of common and individual property at risk. The few who may be aware of the long-term consequences often may lack the ability to make their case to less concerned neighbors.
This issue is one of concern in the field of urban planning because new subdivisions, in particular, often arise at the edge of metropolitan areas in unincorporated county lands or small towns, where governance capacity may be limited and resistance to government regulation particularly high. The result is that oversight is weakest, and the desire for new development highest, precisely where the need for that oversight may be greatest. In regulatory terms, it is the theory of the weakest link. One of our motives for the new report (underwritten by the Federal Emergency Management Agency) is to help shore up those weak links with stronger guidance about sound practices in reviewing plans for new subdivisions. Berding and Weil were serving a similar purpose, at least in the California context, by describing sound practices for community associations, particularly in sustaining adequate reserves for contingencies such as disasters.
But finances are only part of the problem. Sometimes, the leadership of such associations can become so focused on issues like aesthetics and conformity that they lose sight of larger issues like public safety. In the past, the National Fire Protection Association, which supports the Firewise Communities initiative, has trained its attention on the question of covenants that run counter to public safety, for example, by inhibiting well-researched methods for containing wildfire threats. Many of these techniques involve either landscaping or building design, yet some associations have rules limiting tree trimming or landscaping that would aid in wildfire mitigation. In Safer from the Start, NFPA’s 2009 study of the issues involved in building and maintaining “firewise-friendly developments,” a sidebar notes that the state of Colorado’s recently passed “Colorado Common Interest Ownership Act,” among other measures, basically invalidated a number of types of association covenants and restrictions that inhibited defensible space around private dwellings in order to advance wildfire safety statewide. In effect, the state was saying, with regard to rules that made wildfire safety more difficult to enforce, “enough.” At the same time, the publication overall provided a significant amount of sound advice about best practices in wildfire protection in rural subdivisions and new developments.
That seven-year-old NFPA advice recently got a new boost from an interesting direction: Green Builder Media just recently issued its own e-brochure, “Design with Fire in Mind: Three Steps to a Safer New Home,” in cooperation with NFPA. Green Builder Media has more of a direct avenue to influence those developers who want to build safe, resilient, energy-efficient communities.
The fact that these resources have continued to materialize on a regular basis over the past decade or two indicates, to me, that the subject of good design and homeowner association responsibility is not going away any time soon. It is the job of planners, floodplain managers, and local and state officials to ensure that those responsibilities remain on their radar screens and are taken seriously. One-fifth of the American population depends to a significant degree on the quality of their oversight.
Jim Schwab
In a ruling on August 12—just four days ago—the South Carolina Supreme Court, in Columbia Venture v. Richland County, did the nation a great favor that, I suspect, stands little if any chance, in my opinion, of being overturned by the U.S. Supreme Court even if it is appealed by the developer that filed the case against Richland County. The Association of State Floodplain Managers is happy with the decision, as well they should be, having played a role by filing a significant amicus curiae, or “friend of the court” brief on behalf of the county, which includes the state capital of Columbia.
The essence of the case is that Columbia Venture, a joint venture firm led by Burroughs & Chapin, a developer based in the Myrtle Beach area, sued over Richland County’s application of floodplain regulations based on an expansion of the floodway and regulatory floodplain by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) while the firm was acquiring the property from an area farmer about a decade ago. Curiously, Columbia Venture argued that the taking of its property that it alleged began in 2002, at the time FEMA revised its flood maps, as the date the taking occurred, even though it was suing the county for its regulatory actions.
Columbia Venture was clearly hoping to produce a major development in acquiring 4,461 acres of land along the Congaree River for $18 million, although the Columbia Venture was an attempt to muster adequate investment when Burroughs & Chapin had commitments of only $11 million. The farmer selling the property was persuaded to take $6.65 million in shares as part of this process. Columbia Venture was also relying to some extent on public investment in levees under a county resolution that included a number of contingencies that failed to materialize. Those facts helped persuade the court that the company’s investment-backed expectations were unrealistic.
Ultimately, prior to the state high court decision, Columbia Venture sold about two-thirds of its land, mostly to State Rep. Kirkman Finlay, R-Richland, who farms in the area and say he has no plans to develop it. Land that began as farmland apparently will remain in farm use.
Among other points, Columbia Venture alleged that the county’s regulations prohibiting development in the floodway as newly defined by FEMA constituted a flood easement across its property without compensation. Both the trial court referee and the state high court disagreed, noting that any financial losses experienced by Columbia Venture were outweighed by “the important public purposes of mitigating the social and economic costs of flooding” served by the county’s ordinances, which also “further the important federal purposes” of reducing flood losses. Moreover, all county taxpayers and residents benefited “by reducing the County’s potential liability incurred in emergency response, rescue, evacuation, and other actions taken during a flood.”
Indeed. One might think that, in light of all the experience with flood damage of recent decades, this point would not even need to be argued anymore, but apparently some developers are still wont to try. Most, unlike Columbia Venture, are more inclined to recognize a bad or speculative investment in flood-prone land when they see one.
Frankly, the case also recognizes good planning. Rather than elaborate further, I encourage readers to explore the decision and resulting news coverage for themselves. But I will note that a footnote early in the decision quotes the testimony of former Richland County Planning Director Michael Criss with regard to the public safety benefits of the county’s regulations:
The federal flood maps do not account for the continued urbanization and development of the corresponding watersheds and the resulting increase in stormwater runoff and potential flooding . . . . The federal flood maps are not retrospective. They rely on historical flood records and don’t project th potential of increased flooding in the future from urbanization or from the possibility of more intense storms due to climate change.
This is a victory for good floodplain management, sensible planning in the interest of public safety, and for common sense. Supporters of effective hazard mitigation have reason to celebrate.
Jim Schwab
Postscript: The day after I first posted the above article, APA posted on its Recovery News blog my video interview with Chad Berginnis, the executive director of ASFPM, about the new Federal Flood Risk Management Standard. View it here.
 I grew up in suburban Cleveland. After a seven-year hiatus in Iowa and briefly in Nebraska, my wife’s home state, we ended up in Chicago. I am unquestionably a Midwesterner with most of my life lived near the Great Lakes. It will therefore not be surprising that for most of my adult life, I have heard people speculate about moving some of our abundant water to places that have less, mostly in the West. For just about as long, I have been very aware that their speculations were merely pipedreams (pun very much intended).
I grew up in suburban Cleveland. After a seven-year hiatus in Iowa and briefly in Nebraska, my wife’s home state, we ended up in Chicago. I am unquestionably a Midwesterner with most of my life lived near the Great Lakes. It will therefore not be surprising that for most of my adult life, I have heard people speculate about moving some of our abundant water to places that have less, mostly in the West. For just about as long, I have been very aware that their speculations were merely pipedreams (pun very much intended).
Because most people have at most only a cursory understanding of our nation’s intricate water laws and treaties (in the case of the Great Lakes), to say nothing of the costs and challenges of water infrastructure development, I suppose they can be forgiven for their naivete in even entertaining such notions as piping water from Lake Michigan to California. For both legal and practical reasons, the water is not likely any time soon to leave the Great Lakes Basin, let alone find its way to the West Coast. Enough said.
That is all backdrop to noting that, at the moment, Lakes Michigan and Huron, which essentially share identical water levels because they are joined by a strait, are experiencing rising water levels after declining to levels well below average in 2012, in the midst of a drought and high temperatures. The lack of precipitation and high evaporation levels reduced the two lakes to 576 feet above sea level, about 2.8 feet below the average since 1918, when the Army Corps of Engineers began keeping records. All the Great Lakes tend to rise and fall over time, and somewhat in tandem because they are part of a continuous system that flows into the St. Lawrence River and out into the Atlantic Ocean. But Lake Superior is higher before it dumps into Michigan and Huron, which are higher than Lake Erie, and certainly Lake Ontario, which is on the receiving end of Niagara Falls. Gravity is obviously how all this water finds its way to the sea.
High recent rainfall—in June we had seven inches in Chicago with lower temperatures than normal—has kept the lake levels rising. Colder winters because of the polar vortexes have maintained ice cover, reducing evaporation. As a result, the lakes are now three feet higher than they were in 2012. Amid all this rise and fall, some facts should be noted: These lakes are thousands of years old. They are the result of glacial melt as the Ice Age receded, so most of the water is the result not of precipitation but of ancient glacial retreat. And our record keeping is less than a century old, so what we think we know about the long-term fluctuation in water levels, let alone what we can accurately predict about long-term impacts of climate change in the Midwest, remains far less than what we might ideally like to know. There are big gaps in our knowledge that can only partially be filled with other types of scientific analysis.
Nonetheless, based on such limited knowledge, the urge to build on shoreland materializing from nothing more than historical fluctuations sometimes motivates unwise development. Communities along the Great Lakes need to invest in wise lakefront planning that takes those fluctuations into account and does not create new hazards that are sure to arise in the face of lake levels that often rise again faster than we anticipated. Adequate buffers based on such fluctuations must be a part of the zoning and development regulations throughout such areas. It is best we approach what we know about Great Lakes water level fluctuations with a dose of humility and caution, lest nature make a fool of our aspirations.
There are resources for that purpose. Many of the state Sea Grant programs, based at state universities, can offer technical assistance. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, whose Coastal Zone Management Act responsibilities include the Great Lakes, has been developing resources for Great Lakes states. Using NOAA funding, the Association of State Floodplain Managers, with partners like the American Planning Association (APA), has developed, and is still expanding, a website containing its Great Lakes Coastal Resilience Planning Guide. It consists of case studies, a Great Lakes dashboard, and other tools. NOAA’s Digital Coast Partnership has been working with cities like Toledo, Ohio; Duluth, Minnesota; Green Bay, Wisconsin; and Milwaukee to address flooding and development problems along the Great Lakes in varying contexts.
I mention all this because, even amid this temporary abundance of water on the Great Lakes amid a withering drought on the West Coast, water, as always, remains a preoccupying public policy challenge everywhere around the world and across the United States. It is not nearly enough of a focus of public debate, however, and the complexities of the issue seem to evade most people’s attention, including those who ought to be thinking harder about it. Even those who do focus on the question are often siloed into narrow segments of water policy—wastewater, drinking water, flood protection and mitigation, drought planning, coastal zone management, and so forth. We need to approach water challenges more holistically.
APA’s board of directors approached the subject with that larger picture in mind in empowering a special task force to examine the issue. About two months ago, the task force released its report, which began by emphasizing that “water is a central and essential organizing element in a healthy urban environment.” It went on to call for viewing water resource management as “interdisciplinary, not multidisciplinary,” in other words, calling for collaboration among the professions involved. But it also called on the planning profession and university planning schools to provide more training, more education, and more resources centered around the subject of water and its importance to our society. And it calls for APA to “partner with national water service membership agencies” to “foster cross-industry participation and learning opportunities.” It is a far-reaching document that planning leadership in the U.S. is still absorbing, including me. But I commend it as an overdue conversation so that our future conversations about who uses water how, and for what purpose, can be considerably more sophisticated, as they clearly need to be.
We need to move away from pipedreams to serious conversations. Whether in California, where there is too little, or the Great Lakes, where there is currently plenty, we need to get it right because the stakes are high. Very high.
Jim Schwab
 There is something mildly disconcerting about visiting an intriguing city several times without having the spare time to go tourist. I first visited Charleston, South Carolina, in 2003, for a business meeting with the National Fire Protection Association, for which I led an American Planning Association consulting project evaluating the impact of NFPA’s Firewise training program. I wandered a few blocks from the hotel but got only a cursory impression of what the city had to offer. In more recent years, I have been there repeatedly for various meetings and conferences connected to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Coastal Services Center. This led to considerable familiarity with some of the local hotels and restaurants but still did not afford many opportunities to simply wander.
There is something mildly disconcerting about visiting an intriguing city several times without having the spare time to go tourist. I first visited Charleston, South Carolina, in 2003, for a business meeting with the National Fire Protection Association, for which I led an American Planning Association consulting project evaluating the impact of NFPA’s Firewise training program. I wandered a few blocks from the hotel but got only a cursory impression of what the city had to offer. In more recent years, I have been there repeatedly for various meetings and conferences connected to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Coastal Services Center. This led to considerable familiarity with some of the local hotels and restaurants but still did not afford many opportunities to simply wander.
This year, I decided to fix that problem. My wife, Jean, had never been there. We chose our 30th anniversary (June 8) as an excuse for a four-day visit. Besides, it was time for a vacation. Proposals, projects, meetings, and budgets could all wait.
Even as a vacation, it was a view of Charleston through the eyes of an urban planner. None of us leave our experience, knowledge, or even our biases behind. Mine lean toward intellectual inquiry and a fascination with history. Charleston is chock full of history and geographic challenges, which make for interesting environmental history. The old city sits on a once marshy peninsula facing the Atlantic Ocean with the Cooper River to one side, and the Ashley River to the other. Plantations and a thriving rice culture were once built on those foundations. The rice culture, however lucrative it may have been, was built on one other foundation that vanished after the Civil War: slavery. With its demise, and the rise by the late 19th Century of agricultural machinery for rice growing in Texas and Arkansas, rice died as a central feature of the South Carolina economy.
 The story is told vividly in the South Carolina Lowlands exhibit in the Charleston Museum, a two-story building on Meeting Street along what is known as the Museum Mile. As that sobriquet suggests, the city has a great deal to offer in this respect, most of which we did not have the time to visit. The offerings include a Children’s Museum of the Lowcountry, the Confederate Museum, and the Gibbes Museum of Art, currently being renovated, among several others. The Charleston Area Regional Transit Authority makes these attractions readily accessible to visitors with three free trolley lines that come together on John St. in front of the Visitor Center, which sits between King St., largely a commercial corridor, and Meeting St. Of the three, the Green Line (#211) runs the length of the Museum Mile.
The story is told vividly in the South Carolina Lowlands exhibit in the Charleston Museum, a two-story building on Meeting Street along what is known as the Museum Mile. As that sobriquet suggests, the city has a great deal to offer in this respect, most of which we did not have the time to visit. The offerings include a Children’s Museum of the Lowcountry, the Confederate Museum, and the Gibbes Museum of Art, currently being renovated, among several others. The Charleston Area Regional Transit Authority makes these attractions readily accessible to visitors with three free trolley lines that come together on John St. in front of the Visitor Center, which sits between King St., largely a commercial corridor, and Meeting St. Of the three, the Green Line (#211) runs the length of the Museum Mile.
From our perspective, the history of the South Carolina Lowcountry makes up the best piece of the exhibits the Charleston Museum offers, and clearly the most extensive, using a combination of glassed display cases and short videos to tell the story from prehistoric Indian tribes to European settlement and Indian displacement, to colonization, the American Revolution and Civil War, to modern Charleston. Another exhibit, for those more biologically inclined, details the flora and fauna of the region, and two other, smaller exhibits display both the clothing of the area over time, and the furnishings and metalware of the early American presence. It is enough, if one is diligent about it, to occupy the better part of a day. The museum also contains an auditorium for special events.
The museum also owns two old houses that have been preserved and are open to the public. The Joseph Manigault House, named after a French Huguenot descended from religious fugitives to America in the 1600s who became wealthy planters by the early 1800s, was designed by the owner’s brother and completed in 1803 using Adam-style architecture. Among its features is a Gate Temple that was left intact in the mid-20th Century even as an Esso gasoline station operated on the property before the museum finally acquired it well after World War II. During the war, it was used by the USO to entertain service men stationed in Charleston. It is on Meeting St. across a short side street from the Charleston Museum.
The Heyward-Washington House, on the other hand, requires either a long walk down Meeting St. or a ride on the Green Line to the corner of Broad and Church St., at which
point one hikes a block south to a home modestly tucked between other buildings in an area that was urban even when the house was built, just before the American Revolution in 1772. It belonged initially to Thomas Heyward Jr., among other things a signer of the Declaration of Independence, but it never belonged to a Washington. President Washington, during a tour of the southern states in 1791, simply stayed there for one week in June as a guest of the Heywards. More interestingly, the home later became the property of John F. Grimke, who with his wife produced two daughters, Sarah and Angelina, who developed profound differences with their rich, slave-owning, planter parents. The daughters became radical abolitionists. Needless to say, they became less than welcome in South Carolina, which posted a warrant for their arrest. That never happened because they resettled in Philadelphia, where they became Quakers, allied themselves with other abolitionists, and continued their activities, speaking and writing widely for their cause. There is no doubt they remained a thorn in the side of their southern kin until the day they died.
 But by now I am well ahead of, well, our trip. Neither the Charleston Museum nor the two historic homes were among the first things we saw. In fact, we arrived on Sunday, relaxed over brunch at the eminently affordable yet well-managed Town & Country Inn & Suites in West Ashley, a quieter part of the city west of downtown across the Ashley River, and finally made our way across not only the Ashley but the Cooper River, traversing the magnificently attractive Arthur Ravenel Bridge to Patriots Point in Mount Pleasant. The dock is home to the U.S.S. Yorktown, a World War II aircraft carrier now preserved as a museum for visitors. We did not happen to buy tickets for that while we were there, but it does look impressive from dockside.
But by now I am well ahead of, well, our trip. Neither the Charleston Museum nor the two historic homes were among the first things we saw. In fact, we arrived on Sunday, relaxed over brunch at the eminently affordable yet well-managed Town & Country Inn & Suites in West Ashley, a quieter part of the city west of downtown across the Ashley River, and finally made our way across not only the Ashley but the Cooper River, traversing the magnificently attractive Arthur Ravenel Bridge to Patriots Point in Mount Pleasant. The dock is home to the U.S.S. Yorktown, a World War II aircraft carrier now preserved as a museum for visitors. We did not happen to buy tickets for that while we were there, but it does look impressive from dockside.
 We did have tickets for a dinner cruise that evening aboard the Spirit of Carolina, a much smaller vessel designed to provide a pleasant experience for those who like to eat a fine dinner while watching the waves and the birds and the pleasure boats in Charleston Harbor. Both of us enjoyed a well-prepared meal of rib-eye steak, foreshadowed by she-crab soup and a house salad, accompanied by a bottle of champagne provided for our anniversary, and topped off by key lime pie for dessert. To
We did have tickets for a dinner cruise that evening aboard the Spirit of Carolina, a much smaller vessel designed to provide a pleasant experience for those who like to eat a fine dinner while watching the waves and the birds and the pleasure boats in Charleston Harbor. Both of us enjoyed a well-prepared meal of rib-eye steak, foreshadowed by she-crab soup and a house salad, accompanied by a bottle of champagne provided for our anniversary, and topped off by key lime pie for dessert. To  be honest, I do not expect the absolute best of cuisine on dinner cruises; there are some natural limitations built into the format. The cruise is the point of it all. But this was excellent nonetheless. We both came away satisfied. With the help of some gentle guitar music and the breezes that greeted us during our short visit to the upper deck, it was an enjoyable way to celebrate an anniversary. By 9:15 p.m., as our boat pulled ashore to let everyone out, we felt our hosts had treated us to a very pleasant evening.
be honest, I do not expect the absolute best of cuisine on dinner cruises; there are some natural limitations built into the format. The cruise is the point of it all. But this was excellent nonetheless. We both came away satisfied. With the help of some gentle guitar music and the breezes that greeted us during our short visit to the upper deck, it was an enjoyable way to celebrate an anniversary. By 9:15 p.m., as our boat pulled ashore to let everyone out, we felt our hosts had treated us to a very pleasant evening.
The next day our target was the South Carolina Aquarium. Given the geography, and aquatic and maritime history, of Charleston, this aquarium is a natural feature of the city. It is situated on the eastern waterfront of Charleston, a few blocks east of Meeting St., but also accessible by trolley. (It also hosts a parking garage.) One can easily  spend a day there, and we spent most of a day there, absorbing the living exhibits of sea life that give patrons insights into aquatic life of all sizes and the ecological challenges facing much of it today. With such scientific powerhouses as NOAA nearby, one has high expectations of the aquarium for its scientific content, and by and large it delivers. One unusual feature, somewhat removed from its context, is the Madagascar exhibit, including some lemurs in a tree. I do not profess to know how that fits with the rest of the material, but it is edifying nonetheless. One learns of the utterly tiny amount of paved roads on an island nearly the size of Texas with nearly as many people but a declining rainforest. More related to the region, we discovered to our surprise an entire section devoted to piedmont ecology, examining the river life and aquatic ecology of the foothills of the Appalachians. If you can afford the time, the aquarium is well-endowed with such pleasant surprises. We arrived late in the morning but did not leave until about 4 p.m.
spend a day there, and we spent most of a day there, absorbing the living exhibits of sea life that give patrons insights into aquatic life of all sizes and the ecological challenges facing much of it today. With such scientific powerhouses as NOAA nearby, one has high expectations of the aquarium for its scientific content, and by and large it delivers. One unusual feature, somewhat removed from its context, is the Madagascar exhibit, including some lemurs in a tree. I do not profess to know how that fits with the rest of the material, but it is edifying nonetheless. One learns of the utterly tiny amount of paved roads on an island nearly the size of Texas with nearly as many people but a declining rainforest. More related to the region, we discovered to our surprise an entire section devoted to piedmont ecology, examining the river life and aquatic ecology of the foothills of the Appalachians. If you can afford the time, the aquarium is well-endowed with such pleasant surprises. We arrived late in the morning but did not leave until about 4 p.m.
 Although we did not find time to undertake the tour to Fort Sumter, we did visit the Fort Sumter National Monument, a modest building next to the aquarium that houses some displays pertinent to the battle that launched the Civil War when Confederate forces shelled the Union fortress on a small island in Charleston Harbor. Tour boats depart from the piers behind the building, and it is probably worth a visit. I hope to accomplish that on a future trip. The Fort Sumter National Monument, unlike the tour, is free and open to the public, and managed by the National Park Service.
Although we did not find time to undertake the tour to Fort Sumter, we did visit the Fort Sumter National Monument, a modest building next to the aquarium that houses some displays pertinent to the battle that launched the Civil War when Confederate forces shelled the Union fortress on a small island in Charleston Harbor. Tour boats depart from the piers behind the building, and it is probably worth a visit. I hope to accomplish that on a future trip. The Fort Sumter National Monument, unlike the tour, is free and open to the public, and managed by the National Park Service.
 That evening, we cheated, but who cares? We engaged a second establishment, Stars, in helping us celebrate our anniversary, this time on the actual date. I have previously reviewed Stars on this blog. So why not try something new instead? For starters, Jean had never been there; I had been there with colleagues during business trips. After reading my most recent review, Jean insisted she wanted to try the place herself, so I made a reservation. Upon arrival, after checking in with the maître d’, I took her upstairs to see the rooftop bar, where we were promptly served Bellinis, after a short explanation of a drink new to both of us. We loved it. Back downstairs, we got the royal treatment from a waiter who one of the owners subsequently informed us was “Big John,” as opposed to “Little John,” also working there, who was at that moment at the front of the restaurant. Big John had migrated from up north but, for the moment at least, found Charleston to his liking.
That evening, we cheated, but who cares? We engaged a second establishment, Stars, in helping us celebrate our anniversary, this time on the actual date. I have previously reviewed Stars on this blog. So why not try something new instead? For starters, Jean had never been there; I had been there with colleagues during business trips. After reading my most recent review, Jean insisted she wanted to try the place herself, so I made a reservation. Upon arrival, after checking in with the maître d’, I took her upstairs to see the rooftop bar, where we were promptly served Bellinis, after a short explanation of a drink new to both of us. We loved it. Back downstairs, we got the royal treatment from a waiter who one of the owners subsequently informed us was “Big John,” as opposed to “Little John,” also working there, who was at that moment at the front of the restaurant. Big John had migrated from up north but, for the moment at least, found Charleston to his liking.
This time, we diverged in our orders, Jean getting steak (with black truffle grits and bacon braised mushrooms) while I ordered sea scallops. But neither entrée, while excellent, stole the show, at least in our estimate. That honor was reserved for a special share plate that featured cauliflower and broccolini roasted in a cheddar cheese sauce that was as good and succulent as any appetizer I can remember in a long time.
 On Tuesday, our afternoon visit to the Charleston Museum followed a morning visit to the Waterfront Park, much closer to the Battery at the end of the peninsula than to the aquarium and most of Museum Mile, but still accessible by trolley. The park is simply a wonderful outdoor setting in which to view the ocean, complete with fountains, palm trees, and walkways along the water’s edge. It is a very pleasant place to pass some time, especially on a warm summer day. It looks like a wonderful venue for an outdoor wedding and has been used that way. For those who simply want to use their laptop or mobile device while occupying one of many park benches, it is also fully equipped with wifi, courtesy of Google and the Charleston Digital Corridor.
On Tuesday, our afternoon visit to the Charleston Museum followed a morning visit to the Waterfront Park, much closer to the Battery at the end of the peninsula than to the aquarium and most of Museum Mile, but still accessible by trolley. The park is simply a wonderful outdoor setting in which to view the ocean, complete with fountains, palm trees, and walkways along the water’s edge. It is a very pleasant place to pass some time, especially on a warm summer day. It looks like a wonderful venue for an outdoor wedding and has been used that way. For those who simply want to use their laptop or mobile device while occupying one of many park benches, it is also fully equipped with wifi, courtesy of Google and the Charleston Digital Corridor.
Hiking up the street past the old Custom House and turning left at Market St., we reached the popular City Market, a stretch of airy long buildings containing booths featuring numerous local artists and jewelry makers, among others. From one of them I eventually bought a small matte painting of a tropical seashore for my office. It will serve me well on cold Chicago winter days. We also ate lunch at an open air restaurant nearby, the Noisy Oyster, which offered commendable seafood at very reasonable prices. (By this time we were looking to limit both our food expenditures and our caloric intake.) From City Market we took the trolley back to the Visitors Center, where we had parked in the garage for the day, but first took our detour into the Charleston Museum, across the street.
After leaving the museum to get our car, however, we noticed the ominous, heavy gray clouds gathering overhead. Something told us the better part of wisdom lay in returning to our hotel, where we could read our books. (I was working on the H.W. Brands biography of Ben Franklin, The First American. I like to tackle the 700-page heavyweights during vacations.) By the time we arrived at the hotel, the rain was beginning to drip but not coming down very fast. Soon enough, however, the lightning and thunder mounted, and the rain pounded. On the television, we saw news reports from King St. showing cars struggling through several inches of water. I soon learned that much of downtown is either below sea level or at very low elevations with poor drainage, making for a chronic problem of urban flooding. Charleston, also subject to tropical storms such as Hurricane Hugo, which devastated the area in 1989, was not quite the seaside paradise we had enjoyed until then. It is, in fact, one very vulnerable coastal city that also experiences occasional tremors from a fault that triggered a major earthquake in 1886. Charleston needs good disaster plans.
Charleston needs a few other things as well. On our final day, after visiting the Heyward house, we took a long stroll up King St. back in the direction of Stars and the Visitors Center. On a hot day, that can be challenging, so we tried our best to hew to the shady side of the street, though at noon in June, there is a period when no such thing exists. What does exist is a wide variety of old and new storefronts, and we ended up buying some flip-flops and shoes in an H&M store, lunch at the 208 Kitchen, a pleasant little lunch establishment with good sandwiches at single-digit prices, and delicious Belgian gelato at a small store called, well, Belgian Gelato. Eventually, Jean, having finished off her murder mystery, wanted something new to read and found out there was a Barnes & Noble bookstore around the corner from the Francis Marion Hotel, a charming historic place where I have stayed on several previous trips to Charleston. She decided to try Identical by Scott Turow, a Chicago-area writer and fellow member with me of the Society of Midland Authors.
So what does Charleston need? As helpful as the trolley is, and although there is bus service provided by CARTA, it is clear that the creaking, older part of the city is ultimately facing a challenge of mobility as a result of too much dependence on the automobile. Light rail would help, and some people told me it had been discussed, but the big question is how to retrofit it into the existing fabric of this historic core of the city.
 With all the tourism the city is now attracting, it is also facing the classic challenge of most such aging urban magnets of maintaining affordable housing for the workforce it needs to support such attractions within a reasonable distance of their employment. Already there is an obvious outmigration of the working poor to areas like North Charleston, a suburb that has very recently experienced toxic racial tensions between citizens and police, particularly after the shooting of Walter Scott this spring. When we researched hotel prices in preparation for our trip, it became obvious that the downtown area is experiencing significant price escalations. Charleston can easily allow the old city core to become a playground for the affluent, a tax generator as such, but it cannot afford to lose its character in the process. Charleston has come a long way since the lunch counter sit-ins of 1960 and the segregationist politics of Strom Thurmond. The challenge now is to preserve its well-earned reputation by honoring that progress in a progressive fashion. A cursory reading over breakfast of local newspapers told me that issue is far from settled in the development debates that are currently underway.
With all the tourism the city is now attracting, it is also facing the classic challenge of most such aging urban magnets of maintaining affordable housing for the workforce it needs to support such attractions within a reasonable distance of their employment. Already there is an obvious outmigration of the working poor to areas like North Charleston, a suburb that has very recently experienced toxic racial tensions between citizens and police, particularly after the shooting of Walter Scott this spring. When we researched hotel prices in preparation for our trip, it became obvious that the downtown area is experiencing significant price escalations. Charleston can easily allow the old city core to become a playground for the affluent, a tax generator as such, but it cannot afford to lose its character in the process. Charleston has come a long way since the lunch counter sit-ins of 1960 and the segregationist politics of Strom Thurmond. The challenge now is to preserve its well-earned reputation by honoring that progress in a progressive fashion. A cursory reading over breakfast of local newspapers told me that issue is far from settled in the development debates that are currently underway.
Jim Schwab