I was never a New York native, but I did not feel entirely alien, either, when I returned for the first of four visits to the area in January 2013, following Superstorm Sandy. My father lived in Queens most of his life and left only when my mother, who was from Cleveland, insisted on moving. New York City was not to her liking, and she wanted to go home. But my paternal grandparents remained on Long Island until they died in the 1960s, and we often visited. I was born in Bayshore Hospital, one of seven that were evacuated during the storm. My father had told me about living through the “Long Island Express,” the famous 1938 hurricane that also swamped much of New England. I was not a total stranger. I was certainly aware of many of the cultural traits that make New Yorkers famous (or infamous), though I think some consist more of popular stereotype than reality. But there is a certain toughness that comes from living in the Big Apple, even if it’s different from the toughness I have learned from my eventual attachment to Chicago, the alleged “City of Big Shoulders.”
Hence, despite all the vulnerabilities connected with a city of eight million people that is nearly surrounded by water, I instinctively understood the connection of the city with the concept of resilience. The city has withstood more than Sandy—this was the site of the worst 9/11 attacks, after all—and responds well to challenges. There are no feet of clay; the foundation of Manhattan is bedrock. But any map of the city makes clear that every borough but the Bronx is an island, and even that is a peninsula surrounded by water on three sides.
What brought me to New York after Sandy was a decision by the American Planning Association to assist our New York Metro and New Jersey chapters in preparing their members and communities for the arduous task of post-disaster recovery. To be honest, ours was a contribution more of solidarity and expertise than of resources, which had to come from the massive allocations of federal funds used or distributed by federal agencies, led mostly by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) and the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). What mattered to our members was our presence, our ideas, and the time we spent preparing and delivering a series of training workshops in April 2013 on planning for post-disaster recovery. It is fair to say that, as manager of APA’s Hazards Planning Center and the ringleader of that training effort, Sandy recovery dominated my life for the first half of 2013. And this is all context for my observations in reviewing a relatively new book from Island Press, Prospects for Resilience: Insights from New York City’s Jamaica Bay, edited by Eric W. Sanderson, William D. Solecki, John R. Waldman, and Adam S. Parris. Contributors include biologists, geographers, and engineers, among others with a wide range of expertise that contributes to the book’s comprehensive approach. its utility is clearly greater for professional practitioners in planning, civil engineering, public administration, and allied fields, as well as for academic researchers, than for purely casual readers.
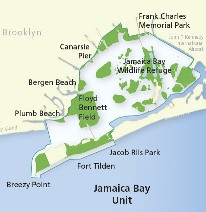
Map from Gateway National Park, National Park Service, website. https://www.nps.gov/gate/planyourvisit/map_jbu.htm
The book focuses specifically on Jamaica Bay, although New York City matters greatly as the municipal government making critical decisions that affect the bay’s resilience. Jamaica Bay, however, is an interesting case study of the intersection of geographic, ecological, industrial, and urban planning factors in both weakening and enhancing the overall resilience of a highly stressed water body and the urban neighborhoods that line its shores. The book’s most noteworthy feature is not any one approach to the subject of resilience for Jamaica Bay, but the way in which it seeks to cross disciplinary lines to undertake a thorough analysis of the prospects for building resilience in an area like Jamaica Bay. Researchers there may have much to share with those examining other ecologically challenged urban water bodies across the nation.
It is important to understand the geographic context of Jamaica Bay, an area familiar to most people (including many New Yorkers) primarily as the scenery below the airplane as it makes its descent into John F. Kennedy International Airport (JFK). The airport, in fact, has a significant impact on Jamaica Bay because it sits at the eastern end of the bay in Queens, the linchpin between the rest of Long Island and the Rockaways, a long, densely populated peninsula that stretches west from JFK and forms the southern boundary of the bay. That, in turn, means that the Rockaways, home to 180,000 people, is extremely vulnerable in a major storm like

Fire devastated Breezy Point during Hurricane Sandy in 2012. Cleanup lasted for months. Photos courtesy of James Rausse.
Sandy. The Rockaways suffered some of the worst damages from the storm, including a fire that tore through Breezy Point, destroying 130 homes. Because of its isolation at the end of the peninsula, and the storm surge that inundated it, it was impossible for fire trucks to respond to the conflagration. For those curious about the origins of a fire in the midst of a flood or hurricane, it is worth remembering that a surge of salt water can easily corrode and short out electrical wires, triggering sparks. Much of New York’s subway system, well designed to pump out normal stormwater, was shut down during Sandy for the same reason.
What makes Jamaica Bay matter enough to devote nearly 300 pages to the subject? It is a great laboratory for resilience. The dense urban development that surrounds the bay stresses the natural ecosystems of the bay, whose biological composition has changed radically over time. The late 19th century witnessed the growth of a viable fishing industry, including oyster harvests, but pollution from sewage disposal and industry brought that to a sudden halt by the 1920s. The same factors reduced the bay’s recreational potential as well. Only in the last few years have there been efforts to restore the oyster beds, but like most such efforts, they will require ongoing research and attention to succeed.
Just as importantly, human communities need to become more resilient as part of a larger social-ecological system because the city is not about to disappear. There simply will be no return to pre-urban conditions. Urban stormwater drainage, sewage disposal, industrial activity, and transportation all have impacts that good urban planning must mitigate or prevent in trying to maintain a healthy urban relationship with the natural environment. Serious scientific inquiry may provide some answers. Greater levels of awareness and connectedness by area residents to the marine environment can also help, but that has often not been the case. An entire chapter explores neighborhood and community perspectives on resilience around Jamaica Bay. Few seasoned urban experts and planners will be surprised to learn that New York generally, and the Jamaica Bay watershed, feature remarkably diverse neighborhoods in terms of density, ethnicity and race, and income level, all of which influence those perspectives and influence community goals. New York is also a remarkably complex city in which residents of some areas in Queens can feel isolated from the center city in Manhattan, but may also feel more secure in their isolation. It is noteworthy that some areas at the western end of the peninsula were heavily populated by public safety personnel. All this influences people’s perspectives on proximity to, and connection with, the waterfront and public understanding of the relationship between human settlement and the ecological health of the bay, which is not always straightforward in any event. People can exert both positive and negative influences on that relationship. The good news is that the authors found that Sandy and the recovery process that followed had some useful impact on the perceptions that underlie those actions.
Given all that complexity, it will also be small surprise that the resilience of Jamaica Bay and its surrounding development is affected by a complex network of overlapping jurisdictional responsibilities that are sometimes in conflict. In addition to the city and its boroughs, a variety of federal and state agencies with varying agendas and authorities, including the New York-New Jersey Port Authority (responsible for airports including JFK), the National Park Service (Gateway National Park), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (climate and coastal zones), overlay the influence of numerous private organizations and academic institutions. Add the flood mitigation and post-disaster recovery responsibilities of FEMA, and one is suddenly confronted with a multicolored collage that for some people can become bewildering.
The case of NOAA is interesting in that climate change is likely to affect the frequency of extreme weather events, which may further test the resilience of an already dynamic social-ecological system. As a scientific agency with significant meteorological and climatological expertise, NOAA has contributed to the array of modeling tools helping to analyze resilience in Jamaica Bay, although academic and other institutions have added to that toolbox. What is important ultimately is to bring together the various strands of research in cooperative efforts for integrative management. The good news, well described toward the end of this book, is that such cooperative efforts have produced the Science and Resilience Institute at Jamaica Bay for that purpose, with participation by decision makers from local, state, and federal agencies to help resolve those conflicting missions and adopt a comprehensive systems approach to the challenges facing the area. Let us hope that those decision makers, and the public officials controlling their resources, have the wisdom to maintain hard-won progress. As is true of many other areas in the U.S., those responsible for the health of Jamaica Bay have much work to do. The rest of us have much to learn from what they are doing and a stake in that progress.
Jim Schwab