In times of political hostility to scientific truth, knowledgeable people sometimes wonder how we can progress without federal support for important initiatives such as adaptation to climate change. The answer, in a vibrant democracy, is that the truth often bubbles up from the bottom instead of being disseminated from the top. When the top is dysfunctional, as it currently seems to be, it is the creativity of local officials and their communities that often saves America from itself. For me, part of the joy of a career in urban planning has been watching and sometimes abetting the great local experiments that pave the way for an eventual federal and international response to pressing urban and environmental problems. The struggle to adapt successfully to climate change is one of those urgent problems. We may indeed confront a wave of scientific ignorance among some leaders in the Trump administration for a few years, but they should be aware that they cannot halt the wave of innovation as communities work to solve real problems.
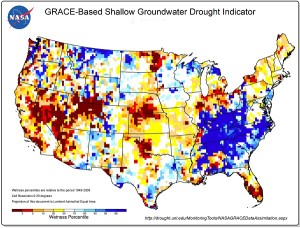
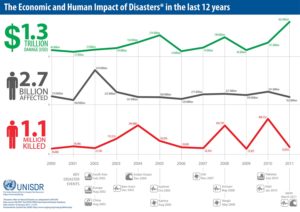
Denying that humans have contributed significantly to climate change through the Industrial Revolution and transportation driven by fossil fuel consumption will do nothing to stop sea level rise, nor will it prevent the bifurcation of extreme weather events that flattens the bell curve with fewer normal events and more high-precipitation storms and prolonged drought, which sometimes also feeds a longer and more intense wildfire season. Disasters happen, and the numbers don’t lie.
 As a result, I was very happy a couple of years ago to be invited to join a Project Advisory Committee for the Kresge Foundation, which had hired Abt Associates to produce a report on climate adaptation at the community level. The foundation has supported a good deal of work related to community resilience and social equity in addition to making serious investments in the resuscitation of Detroit as a functioning urban community. Kresge wants to know what makes communities tick in responding to resilience challenges like climate change, and the study by Abt was intended to establish a sort of baseline for understanding the best practices in local planning related to climate adaptation.
As a result, I was very happy a couple of years ago to be invited to join a Project Advisory Committee for the Kresge Foundation, which had hired Abt Associates to produce a report on climate adaptation at the community level. The foundation has supported a good deal of work related to community resilience and social equity in addition to making serious investments in the resuscitation of Detroit as a functioning urban community. Kresge wants to know what makes communities tick in responding to resilience challenges like climate change, and the study by Abt was intended to establish a sort of baseline for understanding the best practices in local planning related to climate adaptation.
I was thus involved in a series of all-day or multiday meetings of 16 project advisors from around the United States who reviewed and commented on the progress of the study for the consultants. Our meetings involved some serious debates about what constituted climate adaptation and resilience, and the degree to which communities needed to use such labels for what they were doing, or conversely, the degree to which we needed to recognize what they were doing as climate adaptation. Sometimes, we learned, adaptation may quack like a duck without being called a duck by local citizens and officials. What matters is what is accomplished.
Climate Adaptation: The State of Practice in U.S. Communities was officially released by Kresge Foundation in December; I will confess to being a little late in sharing the news, but at the time I was trying to recover from pneumonia. It took me a while longer to find time to read the report in its 260-page entirety, but I thought it important to do so to report intelligently on the final product. There is a difference between reviewing case studies in bits and pieces before committee meetings and seeing the full report between two covers.
I am happy to tell you that I think the nine authors who contributed to the report hit a home run. The bulk of its wisdom lies in 17 case studies spread across the nation, including some surprising places like Cleveland, Ohio, and the Southwestern Crown of Montana. I applaud Abt Associates for its work in even identifying many places that may not have been on the standard maps of leadership in climate resilience. Some of that can be attributed to maintaining an open mind about what they were looking for and what constituted innovation and success in adaptation. One thing that is utterly clear is that no two communities are the same, nor do they face the same problems. Ours is a very diverse country in spite of all that binds us together. Ours is also a nation of creative citizens who confront local problems based on local circumstances rather than “one size fits all” solutions. Perhaps that is why support from Washington does not always matter as much as we think, except in the international arena, where it is critical.
The example of Cleveland may be enlightening in this regard. While issues of social equity may not always seem like a logical starting point for engagement on climate adaptation, Cleveland is a city that was utterly battered by economic change from the 1970s into the early 21st century. The result is a community that is noticeably  less prosperous than its surrounding metropolitan area, and has some of the lowest socioeconomic rankings among major cities nationwide. It is also a city that has lost more than half of its 1950s population, which peaked around 900,000. It is a city that may well say, in evaluating its place on the prosperity scale, “Thank God for Detroit.” That also means that no discussion of climate adaptation will move forward without a solid anchor in efforts to confront these inequities because it is hard to imagine how a community can become resilient in the face of climate challenges without also rebuilding economic opportunity for a badly battered working class. I know. I may have decamped for Iowa in 1979, but I grew up in the Cleveland area and worked my way through college in a chemical plant. Rebuilding prosperity in Cleveland has been tough sledding.
less prosperous than its surrounding metropolitan area, and has some of the lowest socioeconomic rankings among major cities nationwide. It is also a city that has lost more than half of its 1950s population, which peaked around 900,000. It is a city that may well say, in evaluating its place on the prosperity scale, “Thank God for Detroit.” That also means that no discussion of climate adaptation will move forward without a solid anchor in efforts to confront these inequities because it is hard to imagine how a community can become resilient in the face of climate challenges without also rebuilding economic opportunity for a badly battered working class. I know. I may have decamped for Iowa in 1979, but I grew up in the Cleveland area and worked my way through college in a chemical plant. Rebuilding prosperity in Cleveland has been tough sledding.
By the same token, climate change has had a direct impact on Montana, and the Southwestern Crown, a rural area of mountains and forests, has suffered the loss of timber industry jobs, which has in much of the Pacific Northwest resulted in some bitterness toward environmentalists. At the same time, nature takes a serious toll in increased wildfire damage, and at some point, if people of different perspectives can sit down for some serious discussions of reality, they can also imagine new futures for a region at risk. That has been the job of the Southwestern Crown Collaborative.
 Mentioning every case study here would not make sense. But it is worth noting that communities generally seen as not only prosperous but on the cutting edge of the new high-tech economy, such as Seattle, face other challenges that nonetheless tax local resources and resourcefulness. Seattle Public Utilities (SPU) became another Kresge case study, in large part, it seems, because its management needed to find ways to bring its staff and customers into the difficult realm of defining the threat and deciding how it could best be handled. SPU is responsible for managing Seattle’s water supply. When one confronts a future that portends potential water shortages as a result of decreased winter snow pack, leading to reduced snow melt that combined with drought can leave a huge metropolitan area high and dry, the need to recalibrate the system can be daunting. This case study is not important for providing precise answers to such questions, for there are none. Instead, it emphasizes the challenge of accustoming utility engineers and managers to an uncertain future, and helping them find comfort levels with uncertainty. What needs to change to make Seattle’s water supply resilient in the face of natural hazards? How does a city on Puget Sound cope with sea level rise? What plans will be adequate for protecting water supplies two or three decades into the future? In the end, the answers revolve around changing the culture of decision making within the organization as well as communicating those challenges clearly to the public. One product of SPU’s efforts, however, is a path forward for other communities facing similar long-term challenges.
Mentioning every case study here would not make sense. But it is worth noting that communities generally seen as not only prosperous but on the cutting edge of the new high-tech economy, such as Seattle, face other challenges that nonetheless tax local resources and resourcefulness. Seattle Public Utilities (SPU) became another Kresge case study, in large part, it seems, because its management needed to find ways to bring its staff and customers into the difficult realm of defining the threat and deciding how it could best be handled. SPU is responsible for managing Seattle’s water supply. When one confronts a future that portends potential water shortages as a result of decreased winter snow pack, leading to reduced snow melt that combined with drought can leave a huge metropolitan area high and dry, the need to recalibrate the system can be daunting. This case study is not important for providing precise answers to such questions, for there are none. Instead, it emphasizes the challenge of accustoming utility engineers and managers to an uncertain future, and helping them find comfort levels with uncertainty. What needs to change to make Seattle’s water supply resilient in the face of natural hazards? How does a city on Puget Sound cope with sea level rise? What plans will be adequate for protecting water supplies two or three decades into the future? In the end, the answers revolve around changing the culture of decision making within the organization as well as communicating those challenges clearly to the public. One product of SPU’s efforts, however, is a path forward for other communities facing similar long-term challenges.
Bottom line: This report is a great resource for those who want to descend from the heights of overarching theory on climate change to the realities of confronting the problem on the ground. Use this link, download it, and read it. Few resources in recent years have been so thorough in documenting the state of practice in climate adaptation at the local level. I am proud to have been involved even in an advisory capacity. I have learned a great deal from the process.
Jim Schwab