What in the U.S. Midwest would spur comparisons to a hurricane? What could spread damage over an equally wide area? It is a good bet that most people are unfamiliar with the word “derecho,” which comes from Spanish, meaning “straight,” but such a storm made itself felt just three weeks ago in Iowa, Illinois, and Indiana, as well as parts of Nebraska and Wisconsin. The Spanish word with an adopted meaning in English refers to such a storm’s powerful straight-line winds, as opposed to another adapted Spanish word, “tornado,” literally meaning “turned,” which, of course, refers to a cyclonic, or spinning, meteorological phenomenon.
The Event
On August 10, a derecho took shape in eastern Nebraska and the southeastern corner of South Dakota early in the morning. The city of Omaha suffered some of the initial damage, with an estimated 57,000 people losing power. But as it roared across the center of Iowa, the storm, as derechos often do, rapidly gained wind speed until estimated winds of 140 miles per hour struck Cedar Rapids and surrounding Linn County in eastern Iowa. Nearby Iowa City, home of the University of Iowa, also suffered extensive damage. Derechos can and typically do strike with little warning, unlike hurricanes, but even at speeds of 90 to 100 mph, in this case, it still takes hours to cross Iowa from west to east, and even longer to reach Illinois and Indiana.
Thus, my first warning of what was to come, sitting here in Chicago, was a telephone alert from the University of Iowa around noon that day. I get such alerts because I am on the faculty, although I now teach remotely as an adjunct. But our landline and my cell phone are on the system, so the alerts come automatically. Fortunately, that gave me most of the afternoon to prepare for what was coming, which arrived in our area around 3:45 p.m. Winds and rain pounded on our skylights for nearly 45 minutes, leaving numerous branches and twigs on the ground from our stately American elm, which towers above our house and garage and has probably withstood other storms for at least a century. It was already huge when we built our house in 1994, and we chose to make it sure it remained. Even this storm caused it only minor damage.
The same could not be said of many street trees in parts of Chicago. Trees often collapsed on top of parked cars, leaving many owners to bemoan what became of their vehicles—or, in some cases, the roofs of their homes.
Even the repose of the dead was not left undisturbed. Graceland Cemetery, one of the more famous in Chicago, faces months of repairs and replanting and is closed for six weeks. The storm uprooted about 40 trees and damaged numerous gravestones and monuments. It had become a popular place for peaceful strolls and contemplation during the months of coronavirus-induced shutdown. After the storm, it was a visual mess that will cost about $250,000 to repair.

Removing damaged trees in Chicago’s Rogers Park.
One lesser-known by-product of derechos is tornadoes, which can be spun off from the shelf cloud as it moves through an area. In Chicago, two tornadoes, one EF-1 in the Rogers Park neighborhood along Lake Michigan near the city line with Evanston, literally buzzsawed trees in an area of densely built multifamily housing and small

Insurance claims agents inspect building damage in Rogers Park.
businesses. A few days later, I visited the area to shoot photos that appear here. At first, driving up Greenwood Avenue, I wondered where the damage was. But as I drove further north and approached W. Jarvis Ave., the answer became starkly obvious. I could not drive beyond that corner because the street was blocked; Jarvis was one way going east, but Jarvis east of Greenwood was also blocked. City trucks were removing damaged trees. After finding a way to park without impeding traffic, I encountered insurance agents on the ground shooting outside photos of nearby buildings, presumably for damaged masonry. Any damaged cars had already been removed.
That tornado, and another that reportedly skipped across the Eisenhower Expressway (I-290) on the West Side, dramatically demolished for some an old urban myth that tornadoes don’t strike urban areas. People believe this for various reasons, including how they think tall buildings disrupt wind circulation, but trust me: I’ve been involved in disaster recovery long enough to know that tornadoes do not discriminate against smaller towns. Rogers Park is very urban. Tornadoes go where they please. This specific tornado eventually skipped out over the lake, becoming a waterspout. But it left its mark.
The storm, by the way, ultimately spun off at least 17 documented tornadoes, mostly in northern Illinois, but a few in Wisconsin and Indiana. All were either EF-1 or EF-0 on the Enhanced Fujita scale. But by far, most of the damage resulted from the straight-line winds themselves, which were often in the range of 90 to 100 mph, with a top measured speed of 126 mph in Atkins, Iowa, making them basically of tornado or hurricane strength. And they sped, over the course of a single afternoon, across all or parts of several states.
By 4:30, the storm had continued its march into northwest Indiana, where it finally petered out. But what happened along the way?
Iowans can attest that it functioned across much of their state like a Category 2, maybe even Category 3, hurricane. Lyz Lenz, a columnist for the Cedar Rapids Gazette, noted in a guest column for the Washington Post four days later that the winds had damaged “more than 10 million acres, or 43 percent, of the state’s corn and soybean crop.” The reduction in harvest in Iowa is likely to be between one-fourth and one-half. The heading on her column referred to the storm as an “inland hurricane” that most people had not heard about. The damage was massive enough to be visible in satellite images.
The damage was not just to crops on the ground, but to hundreds of millions of bushels in storage bins on farms and in commercial storage facilities, according to the Iowa Department of Agriculture. Toppled grain bins were a common site.

Damage to Chinese House roof in Grinnell. Photo by Rachel Bly.
Despite those staggering figures, that was only the beginning. Between Indiana and Iowa, four people died from either falling trees or electrocution, and, in one case, a mobile home tipped over by high winds. Losses of electric power affected approximately 585,000 Iowans, or roughly 20 percent, while 1.9 million lost power in neighboring Illinois. Tree damage in Linn County totaled in the hundreds of thousands, and most buildings suffered anywhere from mild to catastrophic damage. In small towns, like Grinnell, building damage and tree damage to cars was also extensive. Here, I wish to thank Rachel Bly, director of Conference Operations and Events for Grinnell College, for sending me dozens of photographs she shot after the event. Bly, I might note, has a certificate in emergency management from Park University in addition to her MPA from Drake University. The images she shared help convey some reality to the trauma that occurred. Hundreds of other small communities suffered similar impacts. Not surprisingly, Gov. Kim Reynolds issued a state disaster declaration by August 14 for 25 counties, and has sought a federal declaration from President Trump, citing an estimated $4 billion in damages. By August 19, Trump had signed a declaration for Public Assistance (PA) but not Individual Assistance (IA) for Iowa. PA provides aid for restoring public infrastructure, such as roads and bridges and community facilities, while IA provides direct aid to individuals for reasons such as loss of housing.

Power line damage in Grinnell. Photo by Rachel Bly.

Photo by Rachel Bly

Roof seen through the window. Photo by Rachel Bly.

Inside a damaged salon in Grinnell. Photo by Rachel Bly.
Derechos as a Natural Hazard
All this raises the question of what we know about derechos as a wind-related hazard. I will confess that I spent most of my life never having heard the word, let alone understanding what it meant. It is not the most common occurrence, but it certainly ranks among the most destructive. To my surprise, I learned from Wikipedia that the term was coined in 1888 by a German-American scientist, Gustavus Detlef Hinrichs, who had emigrated to St. Louis just before the Civil War. He wrote in the American Meteorological Journal about a storm that struck Iowa in 1877 and described its unique characteristics. Nonetheless, even in the Midwest today, many people are unfamiliar with the term—until they hear it on the news, as they did on August 10 amid storm warnings.

The gust front “arcus” cloud on the leading edge of a derecho-producing storm system. The photo was taken on the evening of July 10, 2008 in Hampshire, Illinois. Credit: Brittney Misialek. From National Weather Service website.
There are several types of derechos, but the National Weather Service describes a derecho as a “widespread, long-lived windstorm that is associated with a band of rapidly moving showers as thunderstorms.” More specifically, it defines the phenomenon as a swath of damage that “extends more than 240 miles (about 400 kilometers) and includes wind gusts of at least 58 mph (93 km/h) or greater along most of its length.” In plain English, this is a huge, regional storm, not some localized thunderstorm. It exhibits straight-line winds that can be at least double the minimum in the definition, and the August 10 event involved winds far above 58 mph in most locations. Like all such storms, it is a product of unstable atmospheric systems, in this case typically involving a bow-shaped front in a large squall line.
The storms are typically a mid-latitude phenomenon, making North America and the Midwestern U.S. particularly susceptible, but they occur elsewhere in the world as well, including southern latitudes (southeastern Brazil and Argentina), South Africa, China, and even eastern Europe, where a derecho struck parts of Estonia in August 2010, and near Berlin in Germany in 2002. The August 10 event was not the first one I have witnessed in Chicago—another struck in July 2011 and disabled electric power for nearly a million people—but it was certainly the largest in a long time.
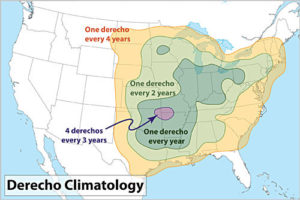
70% of all derechos occur between the months of May-August (the warm season). The other 30% occur during the cool season. From National Weather Service website.
As a mitigation planning response, almost no hazard mitigation plan (produced for FEMA approval as a condition of eligibility for federal hazard mitigation grants) for any state or community east of the Rockies (with the possible exception of Florida) should fail to identify derechos as a potential hazard. Moreover, especially in the Midwest, it may be time for states and communities to reexamine their building codes for wind resistance as a means of limiting future damages from derechos. Finally, it may also be time for many communities to examine more closely their urban forestry programs for adequate attention to hazardous tree management. That does not mean refusing to plant trees or removing them unnecessarily as a mindless precaution. It does mean engaging professional urban foresters in an assessment of the urban tree canopy with an eye to ensuring forest health and removing those trees that are most likely to fail under severe wind pressure. Already, the call has arisen for such reforms in Chicago. It is time for planners, environmentalists, disaster professionals, open space advocates, and concerned citizens to seize the moment while they have the public’s attention.
Jim Schwab


















