
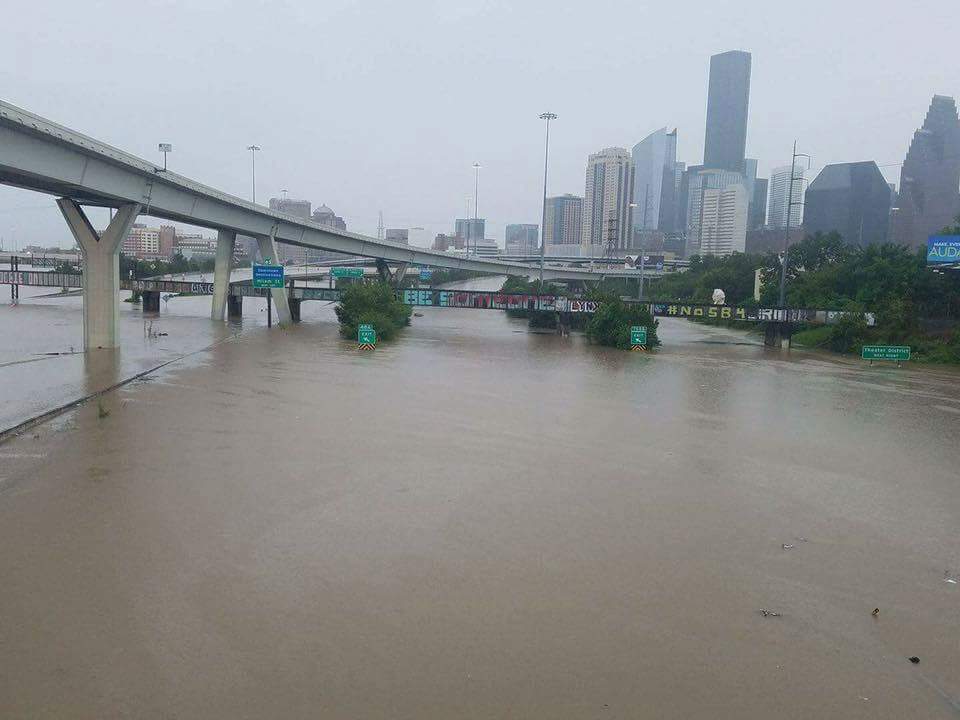
Photo from David Topping’s Facebook posting of his father’s passing.
I first met Ken Topping at the American Planning Association (APA) office in Chicago on a cold day in January 1994. Chicago was suffering one of its classic Arctic blasts at something like -20°F. Ken, a tall, very polite, and articulate gentleman, had his heavy winter coat for the ride back to O’Hare International Airport toward the end of the day. On January 17, just a day or so before he arrived in Chicago, the Northridge Earthquake struck Los Angeles, an area where he had worked for many years. Ken, who was already developing a significant history of advancing what was then the nascent role of urban planning in responding to disasters, became immediately involved. Exactly one year later, on January 17, 1995, the Great Hanshin earthquake leveled much of Kobe, a major city in Japan. With his extensive acquaintances there, Ken was again on the scene.
At the time, I gently needled him that trouble followed him wherever he traveled. But the reality was that Ken took the lead in planning solutions to some of the world’s most vexing environmental challenges: natural disasters. It took years for me to understand the degree to which that initial meeting with Ken changed my life and my perspectives on what I wanted to accomplish as a professional planner. Ken lured me into the world of disaster recovery and resilience planning in a way no one else did.
When we met, it was Bill Klein, then the research director at APA, who introduced us. Just a few months before, Bill, who had somehow negotiated a modest contract with the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) to produce a Planning Advisory Service (PAS) Report on planning for post-disaster recovery, offered me the opportunity to manage the project. This was not because I had any great expertise in the subject. It was because no one else at APA did, either, but I at least had a strong background in environmental planning, and disasters are, at least in part, an environmental problem. Actually, I learned, they are many problems rolled into one, and what I was about to undertake was a challenge well above any I had encountered before, even though I was already completing a book—my second—about environmental justice. But that left the question of why Ken Topping, with noteworthy contributions to the disaster field behind him, should be dealing with a greenhorn like me.
That’s not the way he saw it. Or ever saw it. If Bill had confidence in me, then for Ken it was a chance to mentor someone new to the field and help shape the project at its roots. Over the next few years, as the project grew and expanded from its original ambitions, Ken introduced me to numerous players in this then small arena of planning to reduce the impacts of natural hazards. I did not fully appreciate the significance of some of the people I met, a fact I still regret, but it was all such new territory that I did not always fully understand who was who.
Leaders of Tomorrow
My experience with Ken was far from unique. He mentored, nurtured, and influenced the professional development of people who became some of my best professional friends and colleagues in the growing subfield of hazards planning.

Ken and US-Japan team members meeting with community leaders of the Shin-Nagata North neighborhood that was heavily damaged in the 1995 Kobe earthquake. On the front row from left to right are: Robert Olshansky, Laurie Johnson, Kazuyoshi Ohnishi, and Ken Topping (U.S. team leader). Photo provided by Laurie Johnson.
Robert Olshansky, now professor emeritus at the University of Illinois and living in the Bay Area, met Topping and Laurie Johnson, then a young planner with a bachelor’s degree in geophysics, at a conference of the Central United States Earthquake Consortium in June 1994 in Louisville, Kentucky. The conference, which I also attended, drew mostly engineers, so these three planners “stayed up late in animated conversation,” Rob recalls. Frankly, I don’t remember much of what I did there, but I do recall meeting Laurie either there or a month later at the Natural Hazards Workshop in Boulder, Colorado. I was very much the newcomer to this business back then, in any case. But Rob, Laurie, and Ken engaged in a round of post-Northridge earthquake research meetings in California, which led to a proposal, led by Topping, to compare the Northridge and Kobe earthquake recovery experiences. Eventually funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF), their work began in 1998, but the important facet was that it involved extensive international collaboration between this American trio and four Japanese researchers. It was Ken who introduced Rob and Laurie to Japanese planning. Rob confesses he had never been to Asia before the Kobe earthquake, but he and Laurie developed close connections in Japan who remain good friends 25 years later. Rob says it was Ken who insisted on the close collaboration with the Japanese and helped select the neighborhoods they chose for comparative study.

Ken with the US-Japan team conducting a long-term comparative study of rebuilding in Los Angeles and Kobe following the 1994 and 1995 earthquakes, respectively, during a team meeting in 2000 in Kobe. Left to right are: Robert Olshansky, Laurie Johnson, Ikuo Kobayashi, Hisako Koura, Yoshiteru Murosaki (Japan team leader), Kazuyoshi Ohnishi, and Ken Topping (U.S. team leader). Photo provided by Laurie Johnson.
The remarkable aspect of all this for Laurie Johnson, now a prominent hazard planning consultant based in San Rafael, California, was Ken’s acceptance and support though, she says, “I was barely in my 30s and had only a few years of relevant professional experience” when they first met. Their first contact, she says, came in 1990, when Ken spoke at the International Symposium on Rebuilding after Earthquakes, hosted at Stanford University by Spangle Associates, the firm for which she was then working. Spangle had produced a study that was among the first I studied in this emerging field, examining four case studies of post-disaster recovery. It profoundly influenced my view of what happens to communities in a disaster.
Ken, says Laurie, “wowed the group with his presentation on LA’s efforts to prepare a first-ever, pre-disaster recovery plan for the city before a major disaster like an earthquake struck.” Ken was then the planning director of Los Angeles. Fortunately, a draft of what became the Los Angeles Recovery and Reconstruction Plan had been completed when the Northridge earthquake occurred. The city formally adopted it a year later. Another NSF study led by Spangle Associates, in which Laurie was involved, found “that the plan was instrumental in contributing to the high level of staff performance” after the earthquake, helping most city departments to understand their responsibilities and prepare to perform them.
Innovations
By the mid-1990s, Ken was a tall, white-haired gentleman in his 50s, a strong intellect with a gentle voice. In coming years, in part working on the project I was leading, he made a significant impression on our colleagues at FEMA. Terry Baker, former National Team Leader for Hazard Mitigation Planning, recalled him as “always generous with his time and thoughts. A luminary in the field, although you wouldn’t know that from his kind and down-to-earth demeanor.” Similarly, Cecelia Rosenberg, who served as both project officer and grants manager at FEMA, recalls his “softly persuasive ways and quiet wisdom.” He was never a loud voice, but people knew they were speaking with someone who mattered.
He mattered because of a history of innovations, a willingness to try new things to solve emerging problems. He was well ahead of most planners in recognizing how planning could be used to reduce disaster risk. In a career that that was already well underway amid the environmental planning revolution of the 1970s, he consistently found ways to generate meaningful change. By 1973, he was planning director in San Bernardino County, California, where, as California Polytechnic State University-San Luis Obispo (Cal Poly) Professor William Siembieda notes, he “created one of the first wildfire mitigation programs and an overlay zone on 19,000 square miles of desert land for future regional conservation.”
Ken’s spirit of innovation was not limited to southern California. It was a hallmark of his career. Working with me and a team of contributors to Planning for Post-Disaster Recovery and Reconstruction (PAS 483/484, 1998), his singular contribution lay in crafting a model ordinance for post-disaster recovery that is still in use today. The model offers local governments a means of structuring governance of the recovery process after a major or catastrophic disaster, assigning responsibilities among city agencies and empowering them to handle such urgent tasks as post-disaster demolition and intergovernmental coordination. It helps them create order out of chaos with a management structure for long-term recovery that can be activated as soon as the city declares an emergency. It expedites recovery by saving precious time after disaster strikes. I can state with certainty that no more than a handful of jurisdictions had adopted any similar approach prior to the release of our report.
More than a dozen years later, after I had convinced FEMA to fund an overhaul of the original post-disaster study, adding a bevy of online resources to a new report (Planning for Post-Disaster Recovery: Next Generation, PAS 560, 2014), Ken sought to update the model ordinance as part of the project. When I directed his attention to what I considered an important innovation by the city of Cedar Rapids, Iowa, after its massive 2008 flood, he did not hesitate to contact former Community Development Director Christine Butterfield for details. The new model thus included language requiring municipal licensing of building repair contractors to prevent the sort of fraudulent repairs that had been rife in places like New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina. Ken knew a good idea when he saw one, and Cedar Rapids had done something important. A major contributor to the later PAS Report was Laurie Johnson, who produced two of the most important chapters, dealing with the recovery planning process and implementation of recovery plans. Like me, under Ken’s influence, Laurie had come a very long way in the planning field since first meeting Ken.
Bill Siembieda says this focus on innovation was also evident in Ken’s relationship with Cal Poly, which began in the spring of 2000 and lasted two decades. Ken was a part-time lecturer and George Hasslein Chair in the College of Architecture and Environmental Design, City and Regional Planning Department. His efforts included an international symposium on risk reduction, multidisciplinary courses focused on mitigation and risk reduction, and work with state agencies, most notably on the 2010 California Multi-Hazard Mitigation Plan, in which “he created a set of working groups within the state government” to discuss topics of mutual interest. He believed strongly in the value of cross-disciplinary discussions to achieve a more integrated approach to solving problems.
This focus on integration led to Ken’s involvement in what I regarded as my own signature project, which resulted in the PAS Report, Hazard Mitigation: Integrating Best Practices into Planning (PAS 560, 2010). For his accomplishments and leadership in city planning and management, environmental and hazard resilience planning, Ken was inducted into the College of Fellows of the American Institute of Certified Planners in 2000 and honored with a special session at the 2019 conference of the California chapter of APA.
Multiple Dimensions
Ken died on March 5 from complications of Parkinson’s Disease at 85. He and his wife, Phyllis, spent the last year or so in San Clemente Villas in a seacoast town in Southern California. I had a few last conversations by phone with him after that move from Cambria, California, where he had served at one point as the general manager for the Cambria Community Services District and later chaired the San Luis Obispo County Planning Commission, where he demonstrated his penchant for conservation by helping establish the Fiscalini Ranch as a Pacific Ocean coastal bluff park. Siembieda credits Ken’s “great persistence” and a “willingness to put time and energy into each work product” for his vision to support large solar farms in the county and his opposition to a “large petroleum industry oil train project.”
In one of those calls, he shared with me that he had recently fallen while trying to maneuver his walker in a parking lot. It was clear that time was taking its toll, but in a later call, ever cheerful, he gently told me how much he admired my own career path. He seldom missed an opportunity to encourage the people he had mentored.

Ken with Phyllis, his wife. From David Topping’s Facebook notice about his father’s passing.
One of the more fascinating aspects of his own story, however, was his birth in 1935 in Kobe, Japan, to a pair of American Baptist missionaries. Before the outbreak of World War II, his family found it necessary to return to the United States, where he grew up in San Francisco and Boulder, Colorado, before the family returned to Japan after the war. He later returned to the U.S. for college at the University of Redlands in California, where he met Phyllis, with whom he had two sons, and earned a degree in sociology, followed by further studies at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. They returned to California, where Ken began a career as a regional planner in Los Angeles but also earned a Masters in Public Administration in 1972 from California State University, Los Angeles. That led to his becoming planning director for San Bernardino County in 1973, and later the city of Los Angeles, appointed in 1986 by Mayor Tom Bradley. One of his achievements was Los Angeles’s first zoning update using geographic information systems (GIS), then a new technology.
The environment was clearly one of his high priorities, something readily apparent in April 2012, when he and Phyllis walked my wife, Jean, and me through the Fiscalini Ranch Preserve before treating us to lunch at a local Cambria restaurant. But he also had a deeply empathetic personal side. I had been in Los Angeles the prior week at the APA National Planning Conference (NPC), much of which became for me a daunting experience as I suffered an attack of prostatitis, though I did not know the diagnosis before visiting a local urgent care center. Exhibiting my stubborn streak, on a Saturday evening early in the conference, I showed up in a hotel meeting room after getting dressed, despite feeling drained and weak, to lead a meeting of the project team for the Next Generation project. Ken took one look at me and would have none of it. His personal touch was evident as he turned to Kathy Smith, our FEMA project officer, and said, “Look at him. He’s in no condition to run a meeting.” At Ken’s urging, It was rescheduled subsequently for a remote meeting from Cal Poly the day after our visit to Cambria.

Ken seated along with children and staff at the Morioka Kindergarten in 2013. Photo provided by Laurie Johnson.
Laurie Johnson believes many of Ken’s finer traits can be attributed to his exposure to Japan. She recalls “a beautiful tribute to Ken and his family’s ties to Japan organized by Professor [Haruo] Hayashi (Kyoto University) and colleagues” in March 2013. They were documenting recovery efforts in northern Japan following the 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami, but the group visited a kindergarten founded in the city of Morioka by Ken’s grandmother more than a century earlier. “The kindergartners assembled and tried to sit patiently as the history was explained and Ken was honored,” she says. “They then sang a song, “Small Garden,” that his grandmother had taught her classes many years ago and which classes still sing today.”

From David Topping’s Facebook notice of his father’s passing.
Ken tapped a beat, she says, which reminded her that Ken had taught himself to play the bass and guitar and had played before for the joint research team at home in Cambria in 2002. Music was another element of his humanity and family life (including a family band), and that focus influenced his two sons to pursue careers in music. Ken went on that day at the school to remind the children to continue to learn as they grew up, how he was there himself to learn about the earthquake, and about the value of friends around the world. “So please be my friend, too,” he told them, “and keep learning all of your lives so that you can help make the world a better place.”
Connecting People
As that vignette illustrates, there was nothing more important for Ken Topping than connecting people, particularly people of talent and determination, with the resources and networks they needed to succeed at making the world a better place. And that mission spanned international boundaries.
Professor Norio Maki of Kyoto University was one of those who benefited. He describes Topping as “my mentor on planning.” In addition to working with Ken in Japan, he learned greatly from collaboration on a project in Marikina, a city in the Philippines. The goal was to develop an earthquake mitigation plan through workshops with city staff. In what he describes as “real on-the-job training,” Ken advised him on workshop presentations and the use of GIS. Despite his university degrees, he says, “I think I got my degree in planning from Ken.”
Rob also facilitated Rob Olshansky’s now permanent connection to Japan. Ken helped arrange for Rob to follow him in a one-year visiting fellowship at Kyoto University, with Professor Hayashi. The cultural shift could have been deeply challenging, but Rob brought his children along for “a life-changing year at school in Japan.” Ken advised him on “important Japanese etiquette do’s and don’ts, in addition to navigating the Japanese train system.” Eight years later, Rob was able to pay it forward by doing the same favor for another visiting professor, Jim Goltz. And so the waves of influence move forward. Rob also believes that a book he and Laurie co-authored, After Great Disasters (reviewed on this blog), “would never have happened without Ken’s influence.”
I could go on, and Rob, Laurie, Terry, Cecelia, Bill, and Norio submitted numerous and extensive comments for my use, but the overall point seems clear. Ken is gone, but as with all such special and creative people, the lesson for the rest of us is simple—to continue to extend that positive influence into future generations in our chosen field. And beyond, wherever possible. I hope we are still doing that, in our own ways.
Jim Schwab













![999983_402895306485828_1765724132_n[1]](http://www.jimschwab.com/Hablarbooks/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/999983_402895306485828_1765724132_n1-300x225.jpg)